-
Featured News
Consumer Health: Osteoporosis and exercise
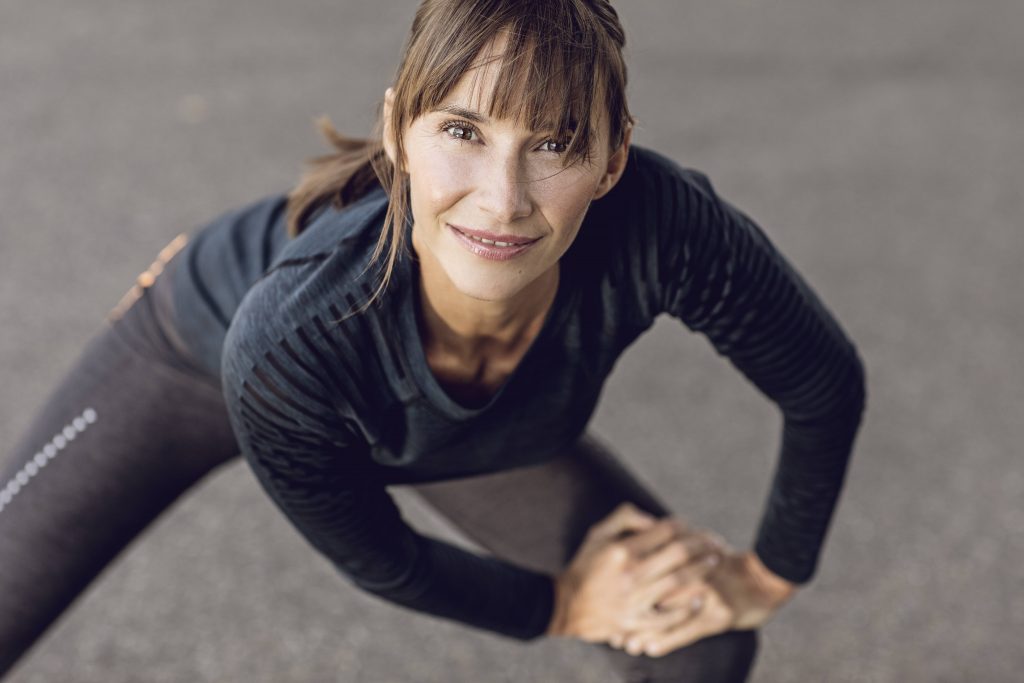

May is National Osteoporosis Awareness and Prevention Month, which makes this a good time to learn more about this bone disease. Osteoporosis affects approximately 10 million people in the U.S., 80% of whom are women, according to the Office on Women's Health.
Osteoporosis causes bones to become weak and brittle — so brittle that a fall or even mild stresses, such as bending over or coughing, can cause a fracture. Osteoporosis-related fractures most commonly occur in the hip, wrist or spine.
Osteoporosis is a major cause of disability in older women. The disease affects men and women of all races. But white and Asian women, especially older women who are past menopause, are at highest risk.
Good nutrition and regular exercise are essential for keeping your bones healthy throughout your life. Exercise can help you build strong bones and slow bone loss. Exercise will benefit your bones no matter when you start, but you'll gain the most benefits if you start exercising regularly when you're young and continue to exercise throughout your life.
If you already have osteoporosis, you might think exercise will lead to fracture. However, using your muscles protects your bones. Certain types of exercise strengthen muscles and bones, while other types are designed to improve your balance — and that can help prevent falls.
The types of activities often recommended for people with osteoporosis include:
- Weight-bearing aerobic activities.
- Flexibility exercises.
- Strength training.
- Stability and balance exercises.
Because of the varying degrees of osteoporosis and fracture risk, your health care professional might discourage you from performing certain exercises.
Connect with others talking about osteoporosis, exercise, and living well in the Bones, Joints & Muscles support group on Mayo Clinic Connect, an online patient community moderated by Mayo Clinic.
Related Articles