-
Research
Ultra-clean rooms are shaping the next generation of biotherapeutics

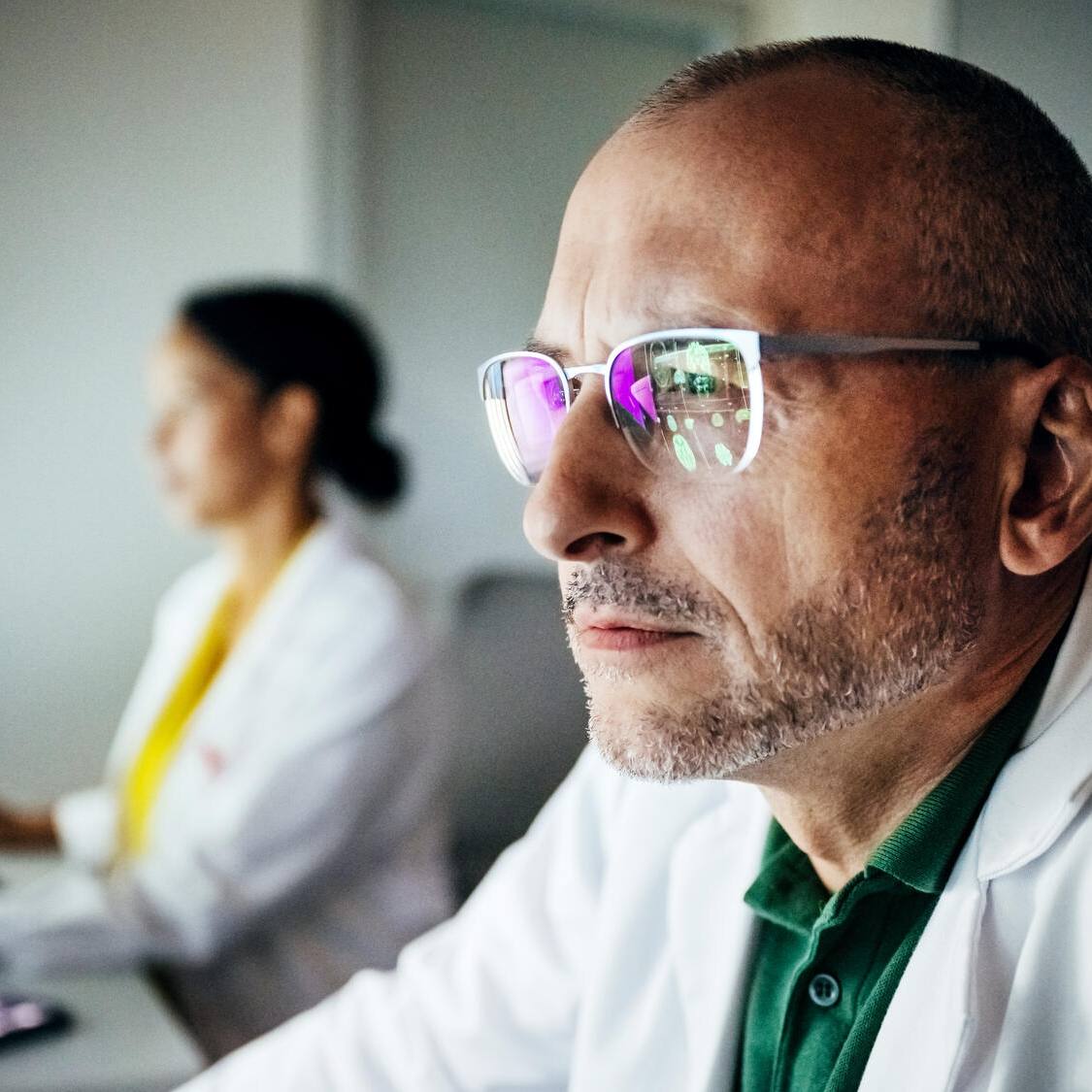
Outfitted in gloves, coveralls, cap, face mask, goggles and even shoe covers, a biomanufacturing engineer moves slowly and deliberately through an ultra-clean space used to manufacture biotherapeutics. This sci-fi-like scene plays out in a "clean room" facility, guided by Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP), to research and develop regenerative biotherapies at Mayo Clinic.
Experimental medicines from the human body such as blood, cells or enzymes are biomanufactured in clean rooms for use in early-stage clinical trials. Mayo Clinic follows stringent CGMP guidelines to ensure the identity, strength, quality and purity of the therapies administered in research studies.
"We're investigating very complex cells as possible therapies for diseases with few or no available treatments. There is no way to advance promising discoveries from the lab to patient care without biomanufacturing in clean rooms," says Henry Walker, a microbiologist in charge of building clean rooms for Mayo Clinic's Center for Regenerative Biotherapeutics. "These facilities enable us to meet strict Food and Drug Administration safety guidelines for first-in-human clinical trials."
An experimental cell-based vaccine for ovarian cancer and new applications for chimeric antigen receptor therapy (CAR-T cell therapy) are two examples of the technologies Mayo Clinic is biomanufacturing in clean rooms. CAR-T cell therapy is a regenerative immunotherapy in which a patient's T cells are genetically engineered to fight cancer.
"Most of the technologies we are biomanufacturing are cell-based and have the potential for targeted healing with few side effects," says Snigdha Rai, senior director of advanced biomanufacturing in the Center for Regenerative Biotherapeutics. "These manufacturing facilities are also designed to handle tissue engineering, 3D bioprinting and cell-free technologies that all have shown promise for repairing diseased cells, tissue and organs."
Video: Biomanufacturing engineers are storing chemical substances in a freezer, preparing the biological safety cabinet for cell work and transferring compounds outside the facility. Before entering the clean room, the photography gear was disinfected, and the staff was dressed in protective coveralls.
What is a clean room?
A CGMP clean room is a highly controlled environment designed to prevent contamination during the drug manufacturing process. The facilities are built with high-powered purification systems that filter out pollutants such as dust, airborne particles, bacteria, fungus, mold and pollen.
"Contaminants harm drug safety and quality so clean rooms' systems constantly filter, clean and monitor the air to ensure a sterile environment. This gives us confidence that we are producing the best possible technologies for research study use," says Walker.
Manufacturing staff must wear head-to-toe "bunny suits" — a type of coveralls—that block the release of bacteria and cells that humans shed.
"Staff conduct their work deliberately, moving about in a one-directional path to minimize shedding particles that could contaminate the air," says Walker. "They are trained to show that they are capable of manufacturing the technology according to safety and quality specifications."
The FDA has the authority to audit the process at any time to ensure compliance and continuous improvement.
On-site biomanufacturing a key advantage
Mayo Clinic has several CGMP facilities used to accelerate biomanufacturing of promising new cell and gene therapies. Mayo hopes to work with industry collaborators and quickly bring new biotherapeutics to market for the benefit of patients everywhere.
At Mayo Clinic, nine clean rooms in Rochester, three in Arizona and four in Florida open new avenues to advance cell-based technologies to clinical trials, providing an advantage that might not be possible when using an outside manufacturer.
"We are seeing a number of requests in which the research team needs a very quick turnaround to protect the integrity of the study," says Rai. "A physician will extract the cells from a patient and needs to have the cells manufactured and given back to that same patient by the end of the day."
Mayo Clinic is committed to the advancement of patient care through the safe biomanufacturing of quality biotherapies for serious and complex diseases.
####
Related stories:
Electrospinning biotherapies of tomorrow
3D bioprinting: transforming medical images into human tissue