-
Cardiovascular
What is a heart arrhythmia?
Heart rhythm problems (heart arrhythmias) occur when the electrical impulses that coordinate your heartbeats don't work properly, causing your heart to beat too fast, too slow or irregularly.
Heart arrhythmias (uh-RITH-me-uhs) may feel like a fluttering or racing heart and may be harmless. However, some heart arrhythmias may cause bothersome — sometimes even life-threatening — signs and symptoms.
Heart arrhythmia treatment can often control or eliminate fast, slow or irregular heartbeats. In addition, because troublesome heart arrhythmias are often made worse — or are even caused — by a weak or damaged heart, you may be able to reduce your arrhythmia risk by adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle.
What's a normal heartbeat?
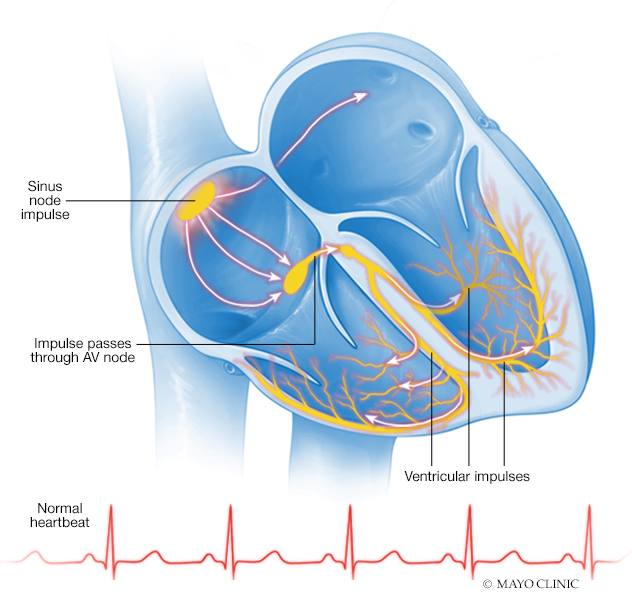
Your heart is made up of four chambers — two upper chambers (atria) and two lower chambers (ventricles). Your heart rhythm is normally controlled by a natural pacemaker (sinus node) located in the right atrium. The sinus node produces electrical impulses that normally start each heartbeat. These impulses cause the atria muscles to contract and pump blood into the ventricles.
The electrical impulses then arrive at a cluster of cells called the atrioventricular (AV) node. The AV node slows down the electrical signal before sending it to the ventricles. This slight delay allows the ventricles to fill with blood. When electrical impulses reach the muscles of the ventricles, they contract, causing them to pump blood either to the lungs or to the rest of the body.
In a healthy heart, this process usually goes smoothly, resulting in a normal resting heart rate of 60 to 100 beats a minute.
Types of arrhythmias
Doctors classify arrhythmias not only by where they originate (atria or ventricles) but also by the speed of heart rate they cause:
- Tachycardia (tak-ih-KAHR-dee-uh). This refers to a fast heartbeat — a resting heart rate greater than 100 beats a minute.
- Bradycardia (brad-e-KAHR-dee-uh). This refers to a slow heartbeat — a resting heart rate less than 60 beats a minute.
Not all tachycardias or bradycardias mean you have heart disease. For example, during exercise it's normal to develop a fast heartbeat as the heart speeds up to provide your tissues with more oxygen-rich blood. During sleep or times of deep relaxation, it's not unusual for the heartbeat to be slower.
Tachycardias originating in the atria include:
- Atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation is a rapid heart rate caused by chaotic electrical impulses in the atria. These signals result in rapid, uncoordinated, weak contractions of the atria.The chaotic electrical signals bombard the AV node, usually resulting in an irregular, rapid rhythm of the ventricles. Atrial fibrillation may be temporary, but some episodes won't end unless treated.Atrial fibrillation is associated with serious complications such as stroke.
- Atrial flutter. Atrial flutter is similar to atrial fibrillation. The heartbeats in atrial flutter are more-organized and more-rhythmic electrical impulses than in atrial fibrillation. Atrial flutter may also lead to serious complications such as stroke.
- Supraventricular tachycardia. Supraventricular tachycardia is a broad term that includes many forms of arrhythmia originating above the ventricles (supraventricular) in the atria or AV node. These types of arrhythmia seem to cause sudden episodes of palpitations that begin and end abruptly.
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. In Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, a type of supraventricular tachycardia, there is an extra electrical pathway between the atria and the ventricles, which is present at birth. However, you may not experience symptoms until you're an adult. This pathway may allow electrical signals to pass between the atria and the ventricles without passing through the AV node, leading to short circuits and rapid heartbeats.
Tachycardias occurring in the ventricles:
- Ventricular tachycardia. Ventricular tachycardia is a rapid, regular heart rate that originates with abnormal electrical signals in the ventricles. The rapid heart rate doesn't allow the ventricles to fill and contract efficiently to pump enough blood to the body. Ventricular tachycardia may not cause serious problems if you have an otherwise healthy heart, but it can be a medical emergency that requires prompt medical treatment if you have heart disease or a weak heart.
- Ventricular fibrillation. Ventricular fibrillation occurs when rapid, chaotic electrical impulses cause the ventricles to quiver ineffectively instead of pumping necessary blood to the body. This serious problem is fatal if the heart isn't restored to a normal rhythm within minutes.Most people who experience ventricular fibrillation have an underlying heart disease or have experienced serious trauma.
- Long QT syndrome. Long QT syndrome is a heart disorder that carries an increased risk of fast, chaotic heartbeats. The rapid heartbeats, caused by changes in the electrical system of your heart, may lead to fainting, and can be life-threatening. In some cases, your heart's rhythm may be so erratic that it can cause sudden death.You can be born with a genetic mutation that puts you at risk of long QT syndrome. In addition, several medications may cause long QT syndrome. Some medical conditions, such as congenital heart defects, may also cause long QT syndrome.
Bradycardia — A slow heartbeat
Although a heart rate below 60 beats a minute while at rest is considered bradycardia, a low resting heart rate doesn't always signal a problem. If you're physically fit, you may have an efficient heart capable of pumping an adequate supply of blood with fewer than 60 beats a minute at rest.
In addition, certain medications used to treat other conditions, such as high blood pressure, may lower your heart rate. However, if you have a slow heart rate and your heart isn't pumping enough blood, you may have one of several bradycardias, including:
- Sick sinus syndrome. If your sinus node, which is responsible for setting the pace of your heart, isn't sending impulses properly, your heart rate may alternate between too slow (bradycardia) and too fast (tachycardia). Sick sinus syndrome can also be caused by scarring near the sinus node that's slowing, disrupting or blocking the travel of impulses. Sick sinus syndrome is most common among older adults.
- Conduction block. A block of your heart's electrical pathways can occur in or near the AV node, which lies on the pathway between your atria and your ventricles. A block can also occur along other pathways to each ventricle.Depending on the location and type of block, the impulses between the upper and lower halves of your heart may be slowed or blocked. If the signal is completely blocked, certain cells in the AV node or ventricles can make a steady, although usually slower, heartbeat.Some blocks may cause no signs or symptoms, and others may cause skipped beats or bradycardia.
Click here to learn more about symptoms, causes, risk factors, prevention and when to see a health care provider.







