-
Featured News
Science Saturday: Exposing toxic protein linked to Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases
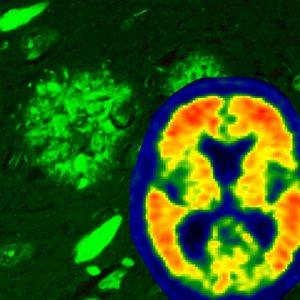
The protein tau has long been implicated in Alzheimer’s and a host of other debilitating brain diseases. But scientists have struggled to understand exactly how tau converts from its normal, functional form into a misfolded, harmful one. Now, researchers at Columbia University’s Zuckerman Institute and Mayo Clinic in Florida have used cutting-edge technologies to see tau in unprecedented detail. By analyzing brain tissue from patients, this research team has revealed that modifications to the tau protein may influence the different ways it can misfold in a person’s brain cells. These differences are closely linked to the type of neurodegenerative disease that will develop — and how quickly that disease will spread throughout the brain.
The study, published today in Cell, employed two complementary techniques to map the structure of tau and decipher the effects of additional molecules, called post-translational modifications (PTMs), on its surface. These new structural insights could accelerate the fight against neurodegenerative diseases, by helping researchers identify new biomarkers that detect these disorders before symptoms arise and design new drugs that target specific PTMs, preventing the onset of disease before it wreaks havoc on the brain.
Read the rest of the article on Advancing the Science.
________________________________________________
Other Mayo Clinic medical research websites:
- Research at Mayo Clinic
- Discovery’s Edge
- Advancing the Science
- Forefront
- Mayo Clinic Center for Individualized Medicine
- Center for Regenerative Medicine
- Center for the Science of Health Care Delivery







