Detecting and treating thoracic aortic aneurysms
Detecting and treating thoracic aortic aneurysms
May 24, 2021
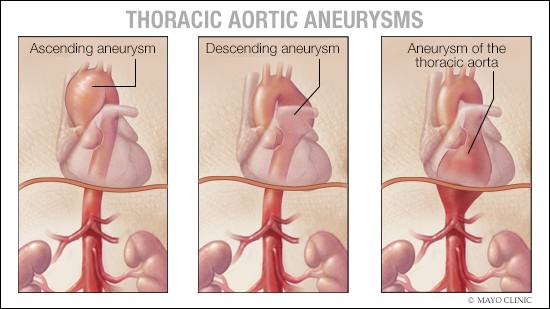
A thoracic aortic aneurysm is a weakened area in the major blood vessel that feeds blood to the body. When the aorta is weak, blood pushing against the vessel wall can cause it to bulge like a balloon. This is called an aneurysm. Depending on the cause, size and growth rate, your thoracic aortic aneurysm treatment options can vary.
Thoracic aortic aneurysms often grow slowly and usually without symptoms, making them difficult to detect. Thoracic aortic aneurysms are often found during routine medical tests, such as a chest X-ray, CT scan or ultrasound of the heart, sometimes ordered for a different reason.
"Most of the time, a thoracic aortic aneurysm is discovered incidentally," says Dr. Gabor Bagameri, a Mayo Clinic cardiovascular surgeon. "When you find out you have an enlarged aorta, it's important to get connected to cardiology and a cardiac surgeon who has expertise and has treated a high volume of patients."




