-
Health & Wellness
What is laryngitis?
 “I lost my voice!” is how people usually describe a condition called laryngitis.
“I lost my voice!” is how people usually describe a condition called laryngitis.
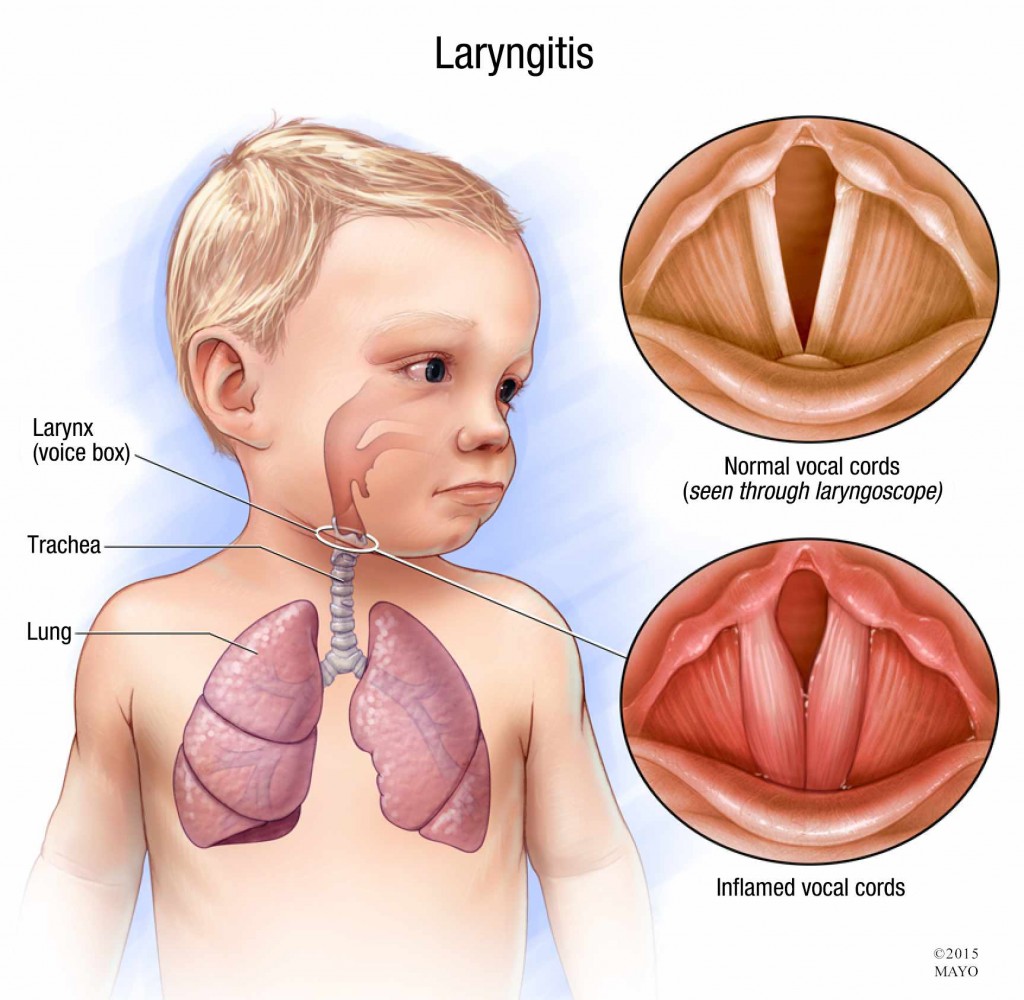
Laryngitis is an inflammation of your voice box (larynx) due to overuse, irritation or infection. The larynx is a framework of cartilage, muscles and mucous membranes that forms the entrance of your windpipe (trachea). Inside the larynx are your vocal cords — two folds of mucous membrane covering muscle and cartilage.
"Normally, your vocal cords open and close smoothly, forming sounds through their movement and vibration," says Kayla Dascher, nurse practitioner at Mayo Clinic Health System. "But when your vocal cords become inflamed or irritated, they swell, causing distortion of the sounds produced by air passing over them. As a result, your voice sounds hoarse. In some cases, your voice can become so faint as to be undetectable."
Laryngitis may be short-lived (acute) or long-lasting (chronic). Although acute laryngitis usually is nothing more than an irritation, persistent hoarseness can signal a more serious problem.
Laryngitis often makes you feel the need to constantly clear your throat. Other signs and symptoms may include:
- Hoarseness
- Weak voice
- Tickling sensation and rawness of your throat
- Sore throat
- Dry throat
- Dry cough
Laryngitis is usually a temporary problem that either improves by itself or clears after treatment. You can manage most acute cases of laryngitis with self-care steps, such as resting your voice, drinking plenty of fluids and sucking on lozenges. If hoarseness lasts for more than two weeks, see your health care provider. If your child develops laryngitis and has a high-grade fever, won’t eat or drink, or has trouble breathing, see your health care provider right away.







