-
Ask the Mayo Mom: Polycystic kidney disease can affect children, too
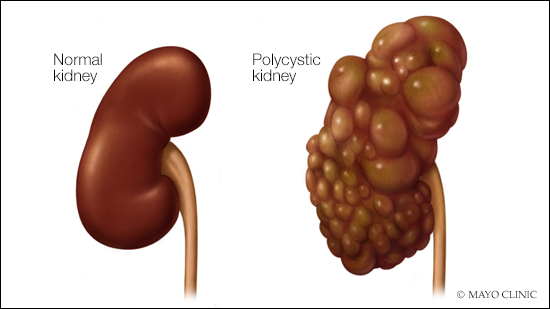
Polycystic kidney disease is an inherited disorder where clusters of cysts develop within the kidneys, causing the kidneys to enlarge and lose function over time. The cysts, which are noncancerous sacs containing fluid, vary in size, and they can grow to be large. This disorder can occur in children and adults.
The two main types of polycystic kidney disease, caused by different genetic flaws, are:
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). Signs and symptoms of ADPKD often develop between the ages of 30 and 40. In the past, this type was called adult polycystic kidney disease, but children can develop the disorder.Only one parent needs to have the disease for it to pass to the children. If one parent has ADPKD, each child has a 50% chance of getting the disease. This form accounts for most of the cases of polycystic kidney disease.
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). This type is far less common than is ADPKD. The signs and symptoms often appear shortly after birth. Sometimes, symptoms don't appear until later in childhood or during adolescence.Both parents must have abnormal genes to pass on this form of the disease. If both parents carry a gene for this disorder, each child has a 25% chance of getting the disease.
Polycystic kidney disease also can cause cysts to develop in the liver and elsewhere in the body. The disease can cause serious complications, including high blood pressure and kidney failure.
The disease varies greatly in its severity, and some complications from polycystic kidney disease are preventable. Lifestyle changes and treatments might help reduce damage to the kidneys from complications, but long-term interventions, including dialysis or kidney transplant, are sometimes needed.
On this special Ask the Mayo Mom edition of the Mayo Clinic Q&A podcast, host Dr. Angela Mattke is joined by Dr. Christian Hanna, a pediatric nephrologist with Mayo Clinic Children’s Center to discuss PKD in children.
For more information and all your COVID-19 coverage, go to the Mayo Clinic News Network and mayoclinic.org.

Related Articles







