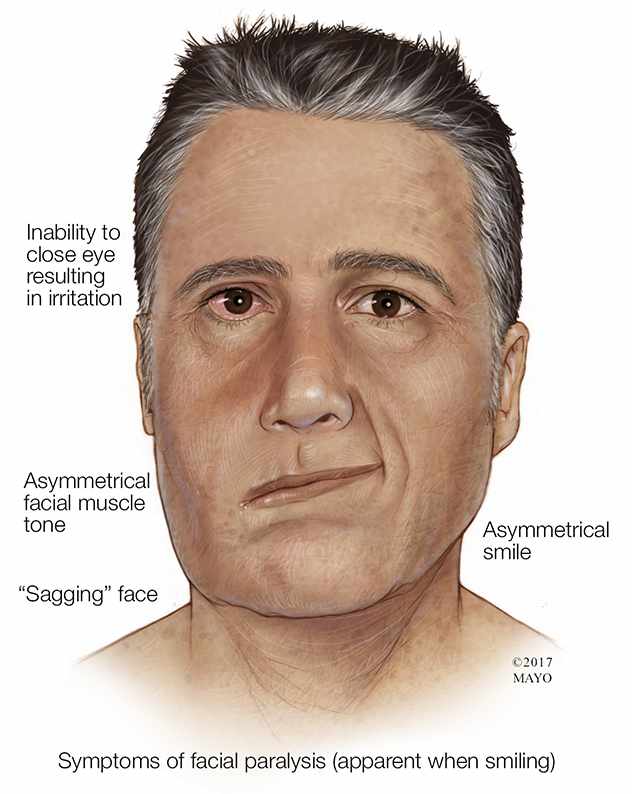
-
Health & Wellness
Consumer Health: 10 ways to avoid complications of diabetes

November is National Diabetes Month, which makes this a good time to learn more about preventing and treating diabetes.
Diabetes mellitus refers to a group of diseases that affect how your body uses blood sugar. The underlying cause of diabetes varies by type. But no matter what type of diabetes you have, it can lead to excess sugar in your blood. Too much sugar in your blood can lead to serious health problems.
The two types of chronic diabetes conditions are Type 1 diabetes and Type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes can develop at any age, although it often appears during childhood or adolescence. Type 2 diabetes, which is more common, also can develop at any age, although it's more common in people over 40.
Prediabetes means you have a higher-than-normal blood sugar level, but it's not yet high enough to be considered Type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes is diabetes diagnosed for the first time during pregnancy, causing high blood sugar levels that can affect your pregnancy and your baby's health.
Long-term complications of diabetes develop gradually. The longer you have diabetes — and the less controlled your blood sugar — the higher the risk of complications. Eventually, diabetes complications could be disabling or even life-threatening.
Following your diabetes treatment plan takes round-the-clock commitment, but your efforts are worthwhile. Careful diabetes care can reduce your risk of serious — even life-threatening — complications.
Here are 10 ways to take an active role in your diabetes care and enjoy a healthier future.
Related Articles