-
Health & Wellness
Diabetes: Testing for Early Indicators
Many people first learn they have diabetes through blood tests done for another condition or as part of a routine physical exam. But in some cases, diabetes may not be detected before damage to your eyes, kidneys or other organs has occurred. That’s why the American Diabetes Association recommends adults have a fasting blood glucose test at age 45. If the test results are normal, repeat the test every three years. If your results are borderline, have a fasting blood sugar test every year. Your health care provider may also test for diabetes based on your symptoms or risk factors.
Mayo Clinic Health System family medicine provider Steven Adamson, M.D., says, "Although the amount of sugar in your blood fluctuates, the range is relatively narrow," says . "After fasting all night, most people have levels between 70 and 100 milligrams of glucose per deciliter of blood (mg/dL). That’s the equivalent of about one teaspoon of sugar in a gallon of water. If you consistently have fasting glucose levels above 125 mg/dL, you likely have diabetes."
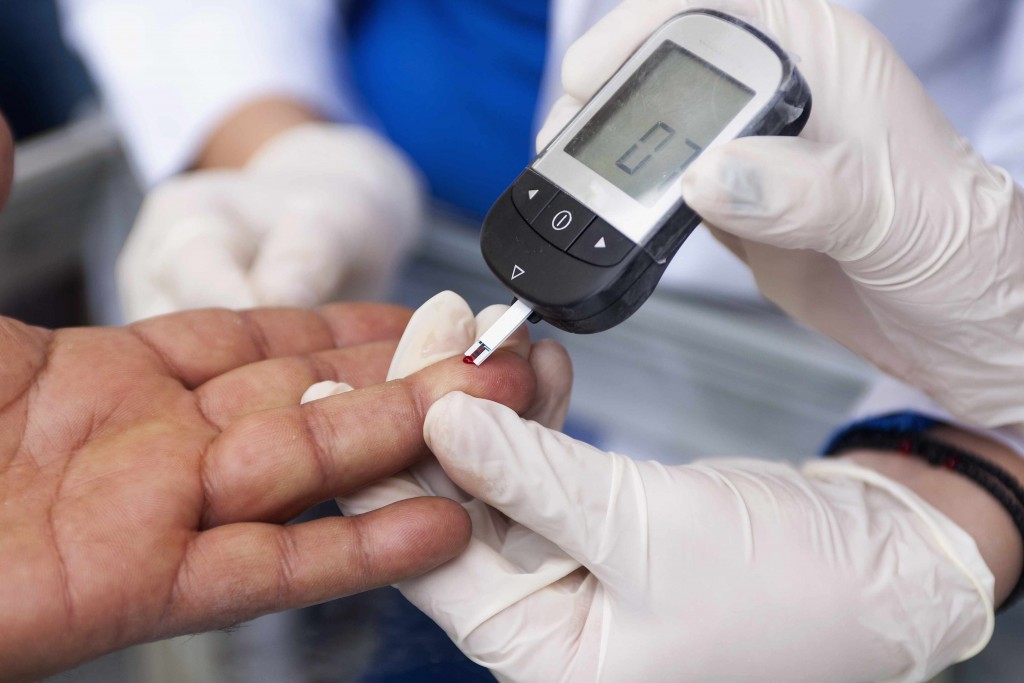
Dr. Adamson shares tests that can detect diabetes:
- Finger-prick blood sugar screening. This test is fast, easy, inexpensive and requires a single drop of blood from a prick in your finger.
- Random blood sugar test. Your blood is drawn through a needle inserted into a vein in your arm and sent to a laboratory for testing. Because you don’t necessarily fast for this test, you may just have eaten and your blood sugar may be high. Even so, it shouldn’t be higher than 200 mg/dL.
- Fasting blood glucose test. In general, your blood sugar is highest right after you eat and lowest after an overnight fast. That’s why the preferred way to test your blood sugar is after you’ve fasted overnight or for at least eight hours. For this test, blood is drawn from a vein in your arm and sent to a laboratory for analysis.
- Glucose challenge test. Often used to screen pregnant women for gestational diabetes, a glucose challenge test requires that you drink eight ounces of an extremely sweet liquid after fasting for six hours. Your blood sugar is measured before you drink the liquid, then every hour for a three-hour period.
- Glycated hemoglobin test. After you’ve received a diagnosis of diabetes, your health care provider may order this test to measure your average blood glucose level for the previous two to three months. The test, also known as a hemoglobin A1C test, measures the amount of blood sugar attached to hemoglobin molecules — the iron-rich molecules in red blood cells that deliver oxygen to your body.
Regular medical checkups can help you and your health care provider spot early indications of diabetes.
Related Articles