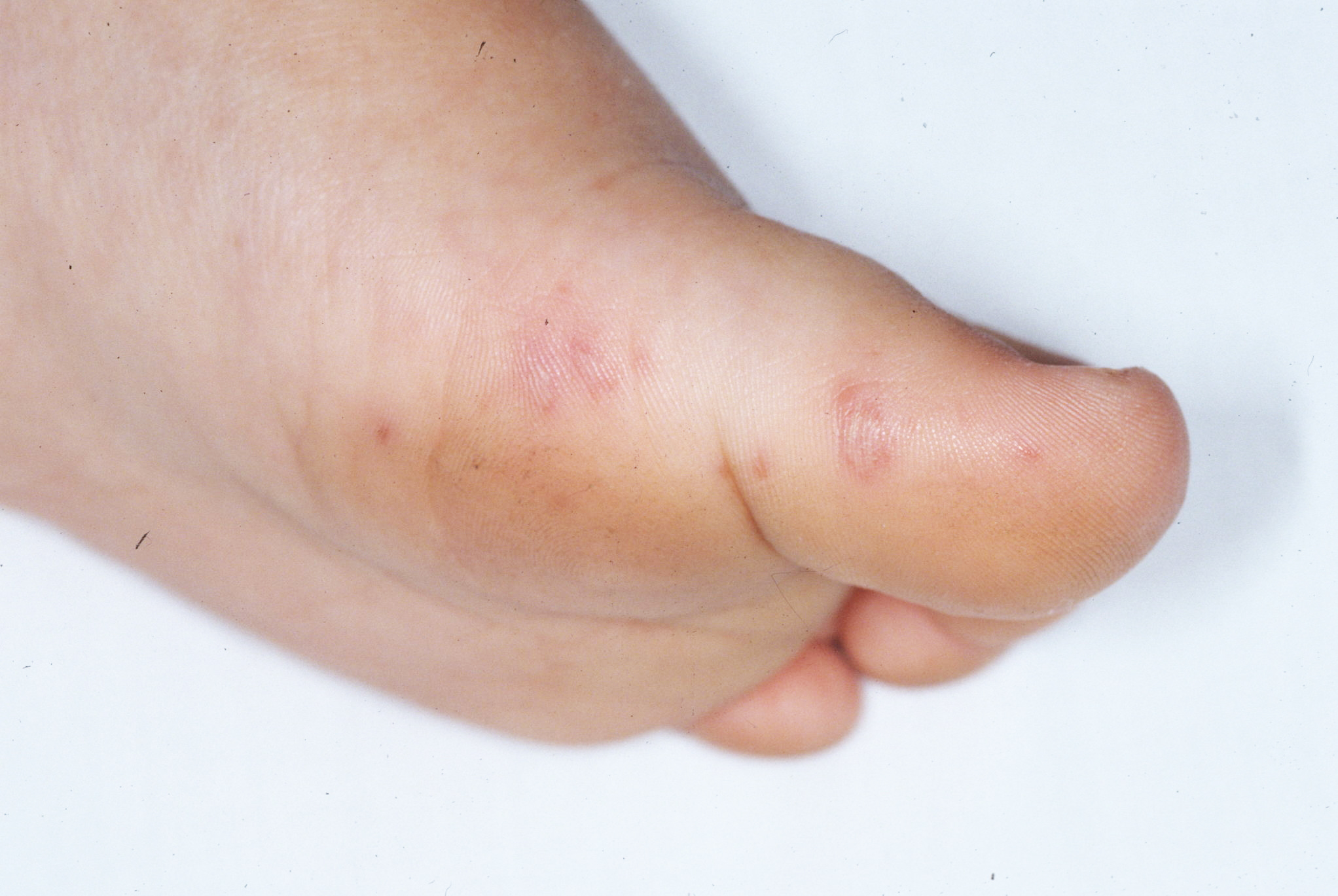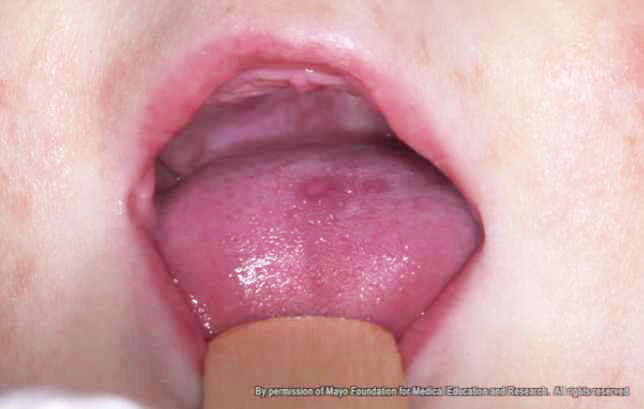
Hand, foot and mouth disease is a highly contagious childhood illness that commonly affects kids ages 5 or under. However, older children and adults also can become sick.
"Hand, foot and mouth disease is usually a viral infection in young children. Initially, they have fevers followed by sores on their hands, feet and mouths, which can sometimes be painful,"says Dr. Pritish Tosh, a Mayo Clinic infectious diseases specialist.
Watch: Dr. Pritish Tosh discusses hand, foot and mouth disease.
Journalists: Broadcast-quality sound bites are in the downloads.
Most people who become infected get better. Rarely does it require hospitalization. Dr. Tosh says hand, foot and mouth disease is self-limiting, meaning there are no medications to treat this infection.
"We do not have medicines for this disease," says Dr. Tosh. "Good supportive care is essential, including ensuring patients have plenty of fluids." Dehydration is a common complication. The disease can cause sores in the mouth and throat, making swallowing painful and difficult.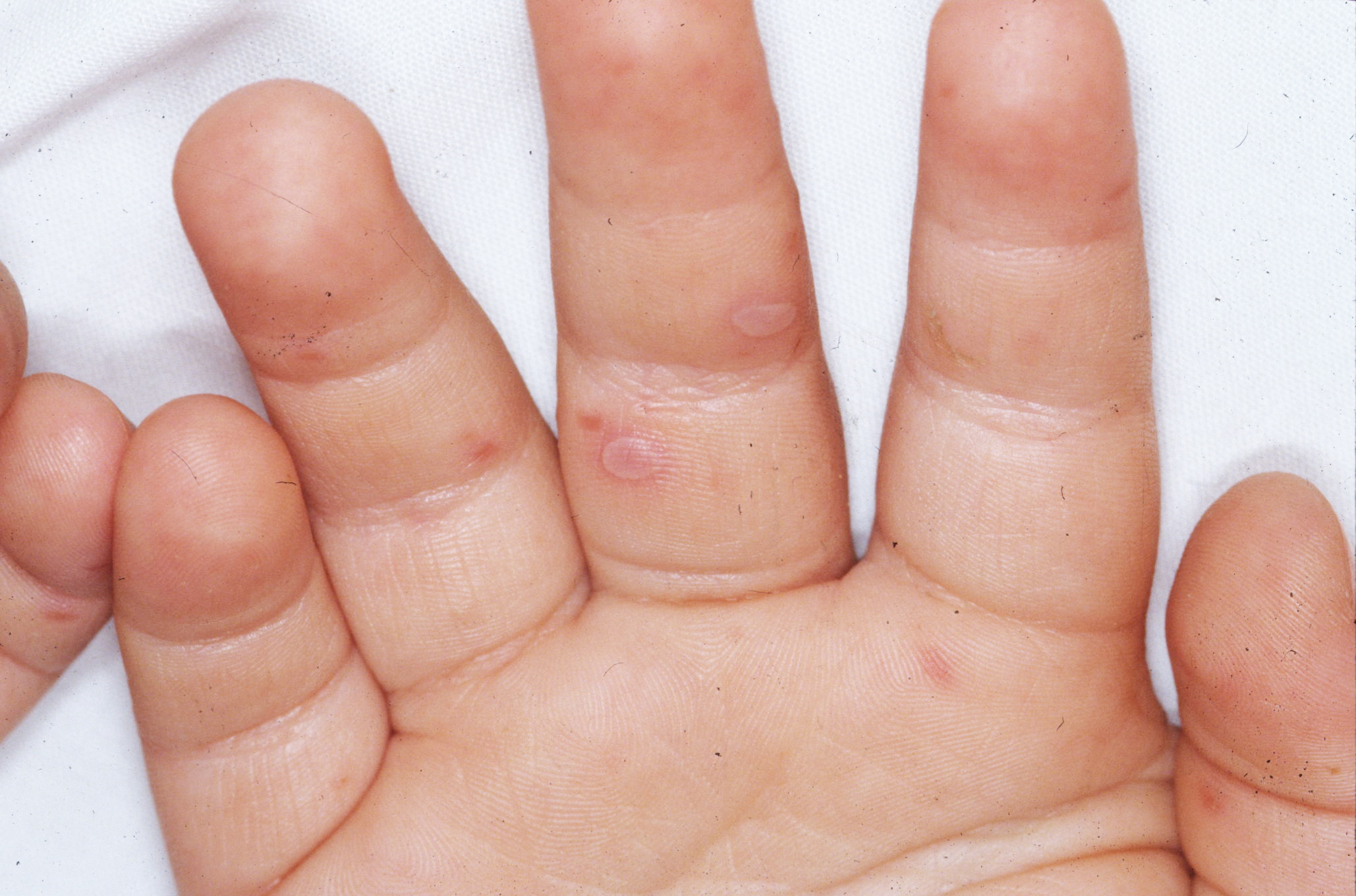
The virus that usually causes hand, foot and mouth disease often is spread through saliva or contact with stool. Practicing good hygiene is important to reducing the risk of contracting this infection.
"A day care setting or in a setting where there are children is a great breeding ground for an outbreak of hand, foot, and mouth disease," says Dr. Tosh. That's because the infection spreads by person-to-person contact, and young children are the most susceptible.
In the U.S., most outbreaks occur in summer or fall months.
Practicing good hygiene is important to reducing the risk of contracting this infection.