-
Innovations in care, treatment improves prognosis for brain tumor patients
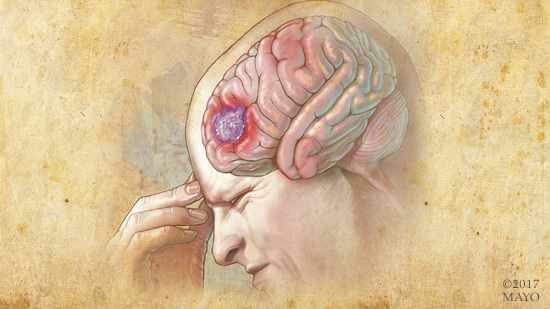
Nearly 80,000 new cases of primary brain tumors are expected to be diagnosed this year in the U.S. A brain tumor is a mass or abnormal growth of cells that can develop from brain cells or cells within structures near the brain.
There are several types of brain tumors. The two most common are gliomas and meningiomas.
“We deal with many different types of brain tumors. The one that’s most challenging to us and the patient is glioblastoma, which is quite aggressive,” says Dr. Ronald Reimer, a neurosurgeon at Mayo Clinic’s Florida campus.
A glioblastoma is a tumor that develops in the supportive tissue of the brain and is usually highly cancerous. Approximately 12,500 new cases are diagnosed each year, says Dr. Reimer.
The symptoms of brain tumor can vary, depending on the size, location and rate of tumor growth.
“We encourage people to seek medical attention if they have had any new type of headache, especially one that’s more intense than in the past, or more protracted in nature. Other concerning symptoms would be new neurologic issues, such as weakness, numbness, confusion or seizures. As well, any alternation in the level of consciousness should be addressed,” says Dr. Reimer.
Treatment options depend on size, type and location of a tumor but typically include surgical removal of the tumor, as well as chemotherapy and radiation.
Innovations in care are resulting in longer survival for brain tumor patients.
At Mayo Clinic, radiation oncologists, neurosurgeons, radiologists, neuro-oncologists, neurologists, medical oncologists and pathologists work together as a team to identify the best treatment options for each patient.
“Many patients can undergo complete tumor removal with excellent results,” says Dr. Reimer.
New surgical techniques are now available for some patients that leave less visible scarring, as well as newer forms of radiation that delivery therapy directly to the tumor site. With stereotactic radiosurgery, for instance, 3-D imaging is used to target high doses of radiation to the affected area with minimal impact on the surrounding healthy tissue.
”Thanks to the many advances in surgery and other therapies, the prognosis for patients with brain tumors has improved in the last decade. We are seeing a dramatic improvement in the two year survival rate of patients, approaching about 40 percent,” says Dr. Reimer. “It’s a very exciting time, being able to offer hope to patients with brain tumors.”







