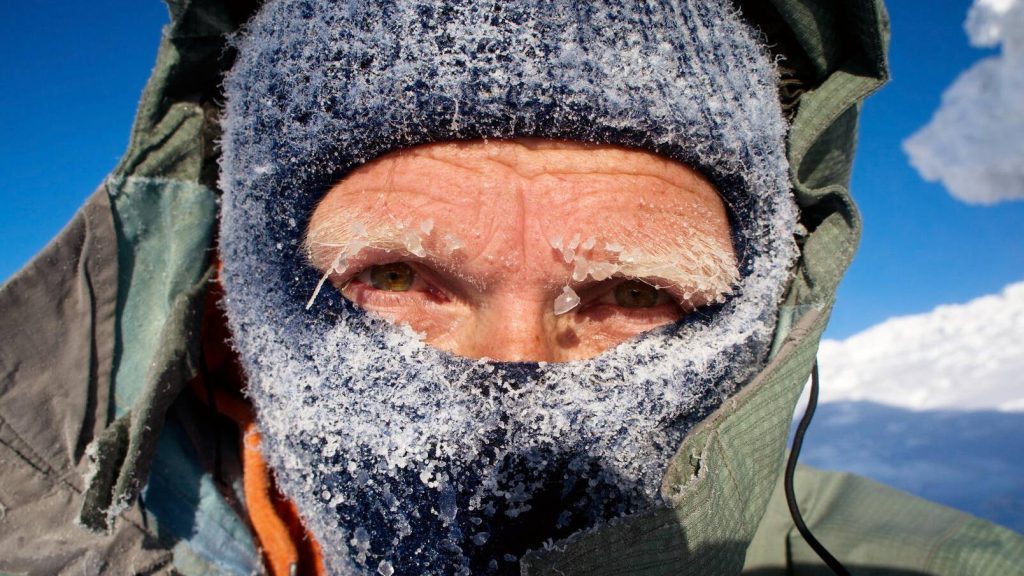
Another winter storm is bearing down on the upper Midwest, with winter storm warnings out for portions of Minnesota, Wisconsin and Iowa. The National Weather Service is calling for heavy snow and gusty winds. Following the snow, the first extreme cold temperatures of the season will arrive, with lows dipping well below zero(fahrenheit) and forecast highs on Sunday and Monday staying in negative territory.
From frostbite to hypothermia, when temperatures get that cold, it can be dangerous. The cold also can affect your lungs.
Can freezing temperatures freeze your lungs?
"Our body does its best to keep our core temperature about 37 degrees(celsius), and our lungs are encased within our thoracic cavity. Unless your whole body is at risk, freezing your lungs should not be at risk," says Dr. Aryan Shiari, a pulmonologist with Mayo Clinic Health System.
He says the cold dry air can enter your lungs and cause irritation, leading to bronchospasm that could cause that tightening sensation of the chest. Your lungs themselves will unlikely freeze.
You may experience discomfort or even a burning sensation from breathing in those bitter cold temperatures. That's common.
"Our bodies are very well designed to adapt to cold air coming in. There are many mechanisms that allow for warming and humidification of the air before it actually hits your lungs where a gas exchange happens," explains Dr. Shiari. "What happens is that cold air is generally drier, and your body works to humidify this. In that process, it can cause irritation to the airways, which results in a process called bronchospasm, where those airways narrow and tighten, and you get that feeling of shortness of breath."
Watch: Dr. Aryan Shiari talks about extreme cold weather and lungs
Journalists: Video is available in the downloads at the end of the post. Please courtesy: Mayo Clinic News Network. Name super/CG: Aryan Shiari, M.D./Pulmonology/Mayo Clinic Health System.
People with chronic lung disease
The extreme cold air can be dangerous for anyone, but for those with chronic lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), the cold can make things feel worse. With emphysema, for instance, the cold air can cause spasms of the bronchial passage, making it more difficult to breathe.
Patients with respiratory disease, whether that's asthma, COPD or other lung diseases, are more prone to have exacerbations of their symptoms if facing cold winter conditions. The best thing that they can do in order to protect themselves is to be prepared. Whether that's having an extra supply of their inhaler regiment for a few days in case of an emergency or having an emergency generator for their medical equipment, such as ventilators, CPAP machines or oxygen concentrators," says Dr. Shiari.
Tips to breathe safely
Dr. Shiari says you should try to avoid being outside during a winter storm. He says if you do have to be outside, follow this breathing advice.
"If you're going to breathe in, generally breathing in through your nose and exhaling through your mouth is better," he says. "Your nose does a better job at humidifying and warming the air than your mouth. Having a scarf to wrap around your nose and mouth, or a ski mask, while outdoors can help, as it can trap some of that heat and moisture."
And try to avoid exercising outside in the cold weather if you suffer from asthma, COPD or chronic lung conditions.
Related posts:
- Cold weather medical emergencies to know about: frostbite and hypothermia
- Mayo Clinic Minute: Safety tips to keep you out of the emergency department this winter.
- Mayo Clinic Minute: Holiday driving safety tips.
For the safety of its patients, staff and visitors, Mayo Clinic has strict masking policies in place. Anyone shown without a mask was either recorded prior to COVID-19 or recorded in a nonpatient care area where social distancing and other safety protocols were followed.