Endometrial cancer, the most common uterine cancer, starts with abnormal cell growth in the endometrium. Significant risk factors include polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and a lack of physical activity, according to a recent study.
PCOS affects 13% of women globally, causing hormonal imbalances, irregular periods, excess androgen and ovarian cysts, which can lead to infertility.
Dr. Kristina Butler, a Mayo Clinic gynecologic oncologist, explains how PCOS increases the risk of endometrial cancer.
Journalists: Broadcast-quality video pkg (1:06) is in the downloads at the end of the post. Please courtesy: "Mayo Clinic News Network." Read the script.
"PCOS is polycystic ovary syndrome, and it's a combination of an excess of androgens, or male circulating hormones, and also menstrual irregularity," says Dr. Butler.
For example, missing your menstrual flow for three months.
"PCOS does increase the risk of endometrial cancer," Dr. Butler says.
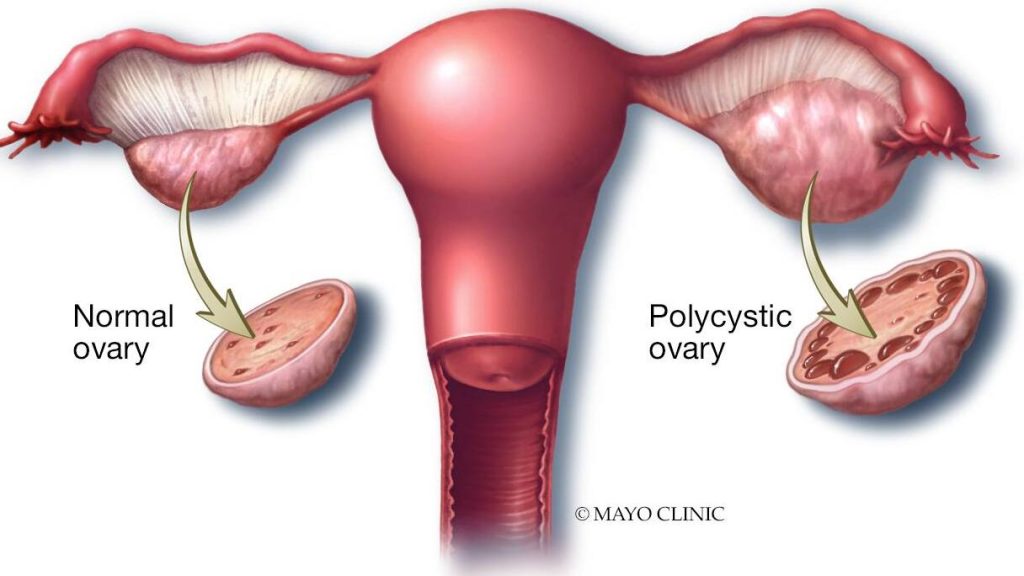
That's because patients with PCOS may miss menstrual cycles.
"This, over time, can lead to thickening of the uterine lining and can predispose a woman to get endometrial cancer," she explains.
Risk factors
Genetics, excess androgen and obesity are risk factors.
"Obesity leads to elevated circulating estrogen levels, which can cause confusion for the menstrual cycle, skipping of menstrual periods and, thus, thickening of the uterine lining," says Dr. Butler.
She says oral contraceptive pills are a principal treatment for PCOS. Combined oral contraceptive pills also can reduce the risk of endometrial, ovarian and colon cancer. And the good news is that, with early diagnosis, endometrial cancer can be treated with surgery.
"We can have an opportunity to really cure women and limit them from needing additional radiation or chemotherapy if it's caught quickly and they have overall very good prognosis long term," says Dr. Butler.
Missed periods can be due to a number of issues, including menopause. Dr. Butler says talk with your healthcare team if you are concerned.
Related posts:
- Mayo Clinic Minute: Health disparities in gynecologic cancers
- Mayo Clinic Minute: Health consequences of obesity







