-
News Cycle
Mayo Clinic Q&A podcast: Caring for veterans
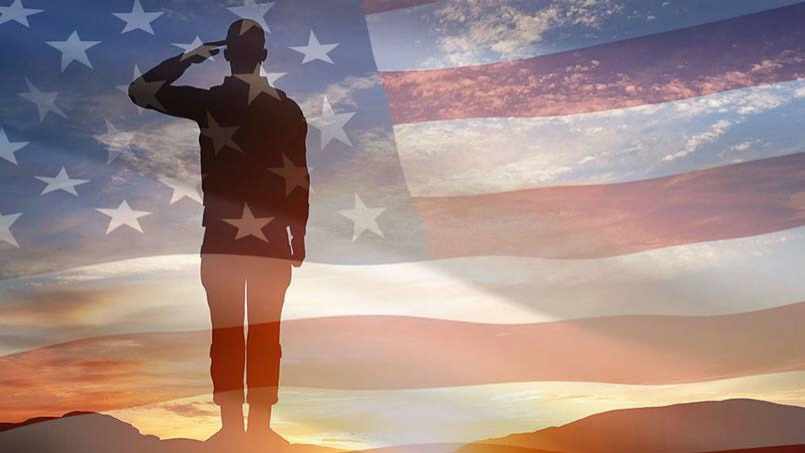

Like all patients, military veterans bring their unique experiences and backgrounds with them as they navigate medical and end-of-life care. At Mayo Clinic, programs are in place to honor military service and care for veterans.
Mayo Clinic Hospice is a partner of the We Honor Veterans Program run by the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization. The Hospice team provides the high level of medical, emotional, spiritual and social care that those who have served in the U.S. armed forces deserve. Team members recognize and honor the hospice patient’s military service with a veteran pinning ceremony. Ceremonies are provided after approval by the patient and family and can include anyone whom the military member and family would like to participate, along with the hospice team.
“It's just a small, simple way of saying thank you to a veteran,” says Loren Olson, a chaplain with Mayo Clinic Hospice. “We bring a pillowcase that represents their branch of the service and a small pin that they could put on a lapel, or a lot of them put them on their military hats. We bring a coin and a certificate from Mayo Clinic expressing our appreciation and we invite them to share their experiences in the military.”
Building on the We Honor Veterans program, Charlie Hall, a Mayo Clinic security operations supervisor, helped develop a "Final Honor Walk" for deceased veterans at his Mayo Clinic Health System location in La Crosse, Wisconsin.
Hall served in the Army as an active-duty rifleman with a combat tour to the Balkans and as a paratrooper with close to 100 military parachute jumps. In addition to his role as a security supervisor, Hall and his team in La Crosse meet with families of deceased veterans to arrange a “Final Honor Walk," where family and staff line the hallway to honor veterans while they are moved out of the hospital room in a flagged-draped cart.
“The final honor walk is something that I wanted to develop,” explains Hall. “I had worked with the We Honor Veterans program in Rochester, with hospice, and the near-end-of-life things with veterans, all the great things they do there. I had the privilege of doing that, but I saw us being able to do a little bit more in an inpatient setting.”
In addition to care at the end of life, it's important to acknowledge the unique needs of veterans every day in the clinical setting. Issues including post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and substance use disorders are more common among veterans than the general population, and they often go hand in hand. More than 2 in 10 veterans with PTSD also have a substance use disorder, according to the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs.
“If a veteran is wearing a hat that signifies their veteran’s status if you will, that to me is the OK to come up and thank them for their service,” says Hall. “And I do that routinely here. It's usually a surprise to the veteran. They're usually extremely grateful. Probably the No. 1 thing is to acknowledge them. It's so important to make people feel at ease when care is coming, especially when there are some complex situations with medical care. There are some very sensitive conversations that have to happen. We all know that happens so much easier when we have great rapport with our patients.”
“Honoring veterans is part of the culture at Mayo Clinic, at least in my experience,” says Olson. “One of the first things I learned as I came to work the hospice program was that We Honor Veterans partnership with the Veterans Administration is important to us. We want to spend time honoring our veterans. So I do think we have developed a corporate culture that just helps us to think of the specific needs of our veterans.”
On this special Veterans Day edition of the Mayo Clinic Q&A podcast, Olson and Hall join host, Dr. Halena Gazelka, for a conversation on caring for veterans.
Watch: Loren Olson and Charlie Hall discuss caring for veterans.
For the safety of its patients, staff and visitors, Mayo Clinic has strict masking policies in place. Anyone shown without a mask was either recorded prior to COVID-19 or recorded in a nonpatient care area where social distancing and other safety protocols were followed.