ROCHESTER, Minn. — New, published data from researchers at Mayo Clinic has found that physical separation reduces the exposure of respiratory droplets and that three feet is helpful but 6 feet separation reduces particle counts to near baseline levels. The findings strongly support the protective value and effectiveness of widespread mask use and maintaining physical distance in helping to stop the spread of the COVID-19 virus.
Watch: Dr. Elie Berbari and Dr. Matthew Callstrom discuss mask study.
Journalists: Broadcast-quality soundbites are in the downloads at the end of the post along with b-roll video of the mask containment study. Please "Courtesy: Elie Berbari, M.D./Infectious Diseases/Mayo Clinic" and "Matthew Callstrom, M.D./Radiology/Mayo Clinic."
"This was an experimental study where we emulated the production of respiratory droplets by using mannequins, that were masked and other mannequins that were unmasked and measured the spread of those droplets at various distances," says Elie Berbari, M.D., chair of the department of infectious diseases at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
Watch: See the mannequins in action.
Researchers measured how effectively masks blocked the number of aerosol particles from a masked source, simulating an individual with a COVID-19 infection, and they simulated the risk of an individual contracting COVID-19, when they were masked.
"We found the most important measure for reducing the risk of exposure to COVID-19 is to wear a mask," says Matthew Callstrom, M.D., Ph.D., chair of the department of radiology at Mayo Clinic in Minnesota. "We found that both disposable paper medical masks and two-layer cloth masks were effective in reducing droplet transmission and we did not find a difference between mask types in terms of how well they blocked aerosol particles emitted by the wearer."

"The most common mechanism for COVID-19 transmission is through respiratory droplets which are larger than aerosols and are more easily blocked with masks," says Dr. Callstrom.
A second part of the study measured aerosol particle counts from a source to a target from one foot to six feet apart, at one-foot intervals. Researchers found that overall, particle counts were reduced with increasing distance which supports current CDC guidance of maintaining physical separation of six feet from others.
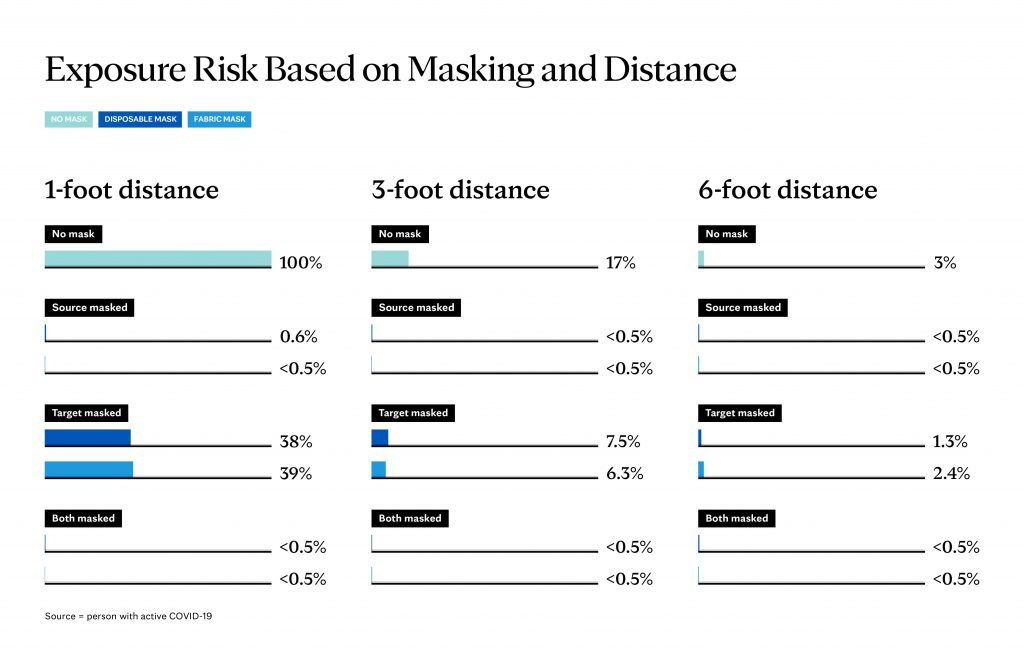
"I think we had some knowledge about the importance of masks and there's been a number of studies that have showed masks are effective in blocking viruses, but what's really important here is just how effective masking is when done by both parties," says Dr. Berbari.
He says additional measures to reduce the risk of transmission include frequent hand washing and use hand sanitizer before and after meals, and after removing masks, and honoring posted room capacities in busy areas.
"We found objectively that masks are critically important for protecting yourself and the people around you," says Dr. Callstrom. "If you're wearing a mask, you're protecting others. If they're wearing masks, they're protecting you."
###
About Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic is a nonprofit organization committed to innovation in clinical practice, education and research, and providing compassion, expertise and answers to everyone who needs healing. Visit the Mayo Clinic News Network for additional Mayo Clinic news and Mayo Clinic Facts for more information about Mayo.
Media contact:
- Joe Dangor, Mayo Clinic Public Affairs, newsbureau@mayo.edu
For the safety of its patients, staff and visitors, Mayo Clinic has strict masking policies in place. Anyone shown without a mask was recorded prior to COVID-19 or recorded in an area not designated for patient care, where social distancing and other safety protocols were followed.







