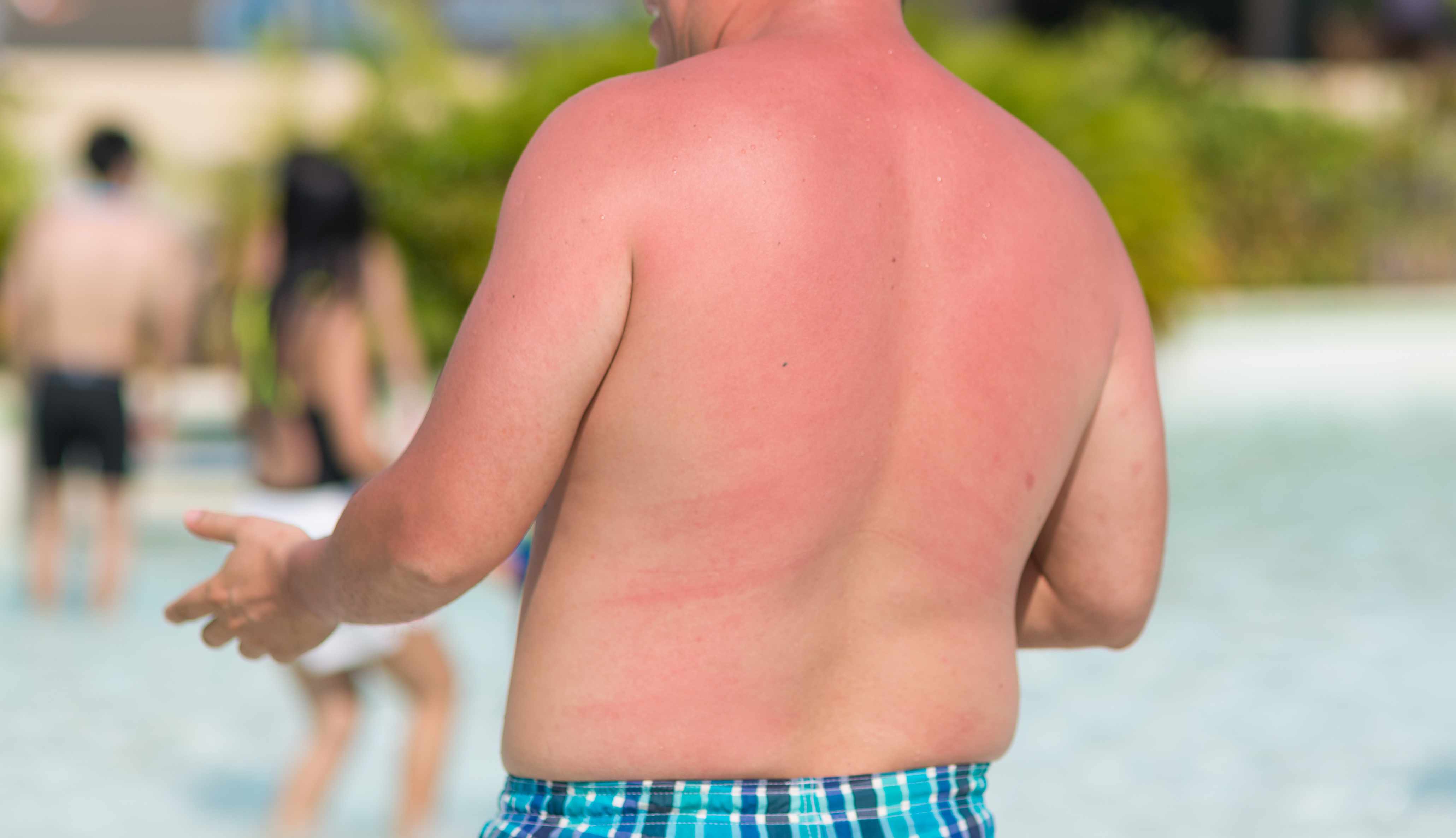
By 65, Caucasian men are reportedly twice as likely as women to get melanoma. And not only are they more likely to develop melanoma, but also they often have a more aggressive form of the disease, according to a report from Blue Cross Blue Shield Association.
"Melanoma is often believed to be 'just another skin cancer,'” says Dr. Svetomir Markovic, an oncologist at Mayo Clinic not involved with the report. "Unfortunately, this is not true."
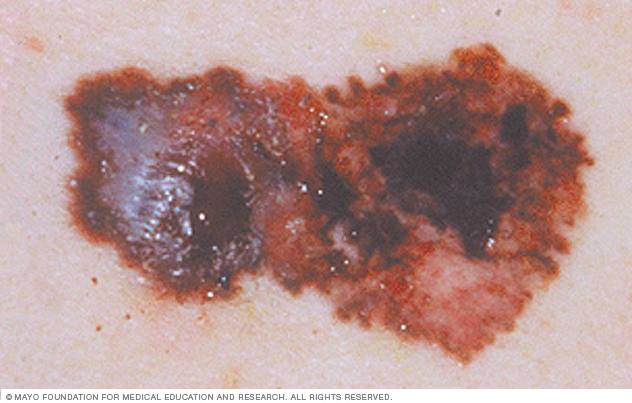
Melanoma, the most serious type of skin cancer, develops in the cells (melanocytes) that produce melanin — the pigment that gives your skin its color. Melanoma also can form in your eyes and, rarely, in internal organs, such as your intestines.
According to a 2016 report in Nature, "Differences in the expression of a particular gene could explain why men with skin cancer tend to have a lower survival rate than women." The Skin Cancer Foundation agrees, noting that, "Genetics may play a larger role in mortality among men than previously thought."
There could be other reasons contributing the gender difference. "We don’t have a clear explanation for this difference, but what likely plays a significant role is that men are far less engaged in health care than women," says Dr. Markovic. This mean that they sometimes don't see a health care provider until the disease is in advanced stages.
Dr. Markovic also says that men traditionally may have outdoor occupations that expose them to the sun, and they could be less likely to use sunscreen. "Pollution and the diminishing ozone layer in the atmosphere could contribute, as well," adds Dr. Markovic.
Learn more about melanoma
Melanomas also can develop in areas of your body that have little or no exposure to the sun, such as the spaces between your toes and on your palms, soles, scalp or genitals. These are sometimes referred to as hidden melanomas because they occur in places most people wouldn't think to check. When melanoma occurs in people with darker skin, it's more likely to occur in a hidden area.
Hidden melanomas include:
- Melanoma under a nail
Acral-lentiginous melanoma is a rare form of melanoma that can occur under a fingernail or toenail. It also can be found on the palms of the hands or the soles of the feet. It's more common in blacks and in other people with darker skin pigment. - Melanoma in the mouth, digestive tract, urinary tract or vagina
Mucosal melanoma develops in the mucous membrane that lines the nose, mouth, esophagus, anus, urinary tract and vagina. Mucosal melanomas are especially difficult to detect because they can easily be mistaken for other far more common conditions. - Melanoma in the eye
Eye melanoma, also called ocular melanoma, most often occurs in the uvea — the layer beneath the white of the eye (sclera). An eye melanoma may cause vision changes and be diagnosed during an eye exam
The exact cause of all melanomas isn't clear, but exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight, or tanning lamps and beds increases your risk of developing melanoma. Limiting your exposure to UV radiation can reduce your risk of melanoma.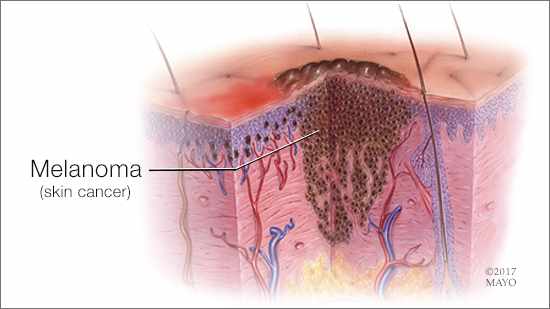
Factors that may increase your risk of melanoma include:
- Fair skin
Having less pigment (melanin) in your skin means you have less protection from damaging UV radiation. If you have blond or red hair, light-colored eyes and freckles, or sunburn easily, you're more likely to develop melanoma than is someone with a darker complexion. But melanoma can develop in people with darker complexions, including Hispanics and blacks. - A history of sunburn
One or more severe, blistering sunburns can increase your risk of melanoma. - Excessive UV light exposure
Exposure to UV radiation, which comes from the sun, and tanning lights and beds can increase the risk of skin cancer, including melanoma. - Living closer to the equator or at a higher elevation
People living closer to the earth's equator, where the sun's rays are more direct, experience higher amounts of UV radiation than those living in higher latitudes. In addition, if you live at a high elevation, you're exposed to more UV radiation. - Having many moles or unusual moles
Having more than 50 ordinary moles on your body indicates an increased risk of melanoma. Also, having an unusual type of mole increases the risk of melanoma. Known medically as "dysplastic nevi," these tend to be larger than normal moles, and have irregular borders and a mixture of colors. - A family history of melanoma
If a close relative, such as a parent, child or sibling, has had melanoma, you have a greater chance of developing melanoma, too. - Weakened immune system
People with weakened immune systems, such as those who've undergone organ transplants, have an increased risk of skin cancer.







