-
Featured News
Pneumonia and the ‘walking’ kind
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus (purulent material), causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. A variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses and fungi, can cause pneumonia. Pneumonia can range in seriousness from mild to life-threatening. It is most serious for infants and young children, people older than age 65, and people with health problems or weakened immune systems.
[This medical information can be found on mayoclinic.org.]
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of pneumonia vary from mild to severe, depending on factors such as the type of germ causing the infection, and your age and overall health. Mild signs and symptoms often are similar to those of a cold or flu, but they last longer.
Signs and symptoms of pneumonia may include:
- Chest pain when you breathe or cough
- Confusion or changes in mental awareness (in adults age 65 and older)
- Cough, which may produce phlegm
- Fatigue
- Fever, sweating and shaking chills
- Lower than normal body temperature (in adults older than age 65 and people with weak immune systems)
- Nausea, vomiting or diarrhea
- Shortness of breath
Newborns and infants may not show any sign of the infection. Or they may vomit, have a fever and cough, appear restless or tired and without energy, or have difficulty breathing and eating.
Walking pneumonia is an informal term for pneumonia that isn't severe enough to require bed rest or hospitalization. You may feel like you have a cold. The symptoms are generally so mild that you don't feel you need to stay home from work or school, so you are out walking around. Chances are you won't see a doctor for your mild symptoms. If you do see a doctor, you may not seem sick enough to need a chest X-ray, which is the way to diagnose any kind of pneumonia.
Walking pneumonia is often caused by a type of bacterium that produces milder symptoms that come on more gradually than do those of other types of pneumonia. The illness often is brought home by young children who contract it at school. Family members of infected children typically begin having symptoms two or three weeks later. This kind of pneumonia can be treated with an antibiotic.
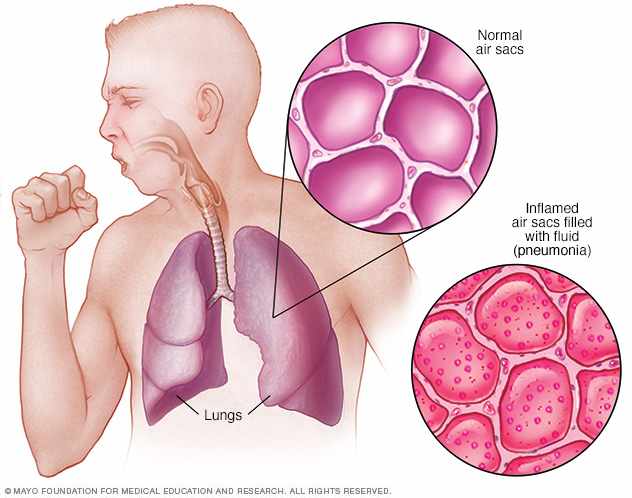
Pneumonia and your lungs
Most pneumonia occurs when a breakdown in your body's natural defenses allows germs to invade and multiply within your lungs. To destroy the attacking organisms, white blood cells rapidly accumulate. Along with bacteria and fungi, they fill the air sacs within your lungs (alveoli). Breathing may be labored. A classic sign of bacterial pneumonia is a cough that produces thick, blood-tinged or yellowish-greenish sputum with pus.