-
Ulcerative colitis can be debilitating
Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes long-lasting inflammation and ulcers (sores) in your digestive tract. Ulcerative colitis affects the innermost lining of your large intestine (colon) and rectum. Symptoms usually develop over time, rather than suddenly.
Ulcerative colitis can be debilitating and can sometimes lead to life-threatening complications. While it has no known cure, treatment can greatly reduce signs and symptoms of the disease and even bring about long-term remission.
Symptoms
Ulcerative colitis symptoms can vary, depending on the severity of inflammation and where it occurs. Signs and symptoms may include:
- Diarrhea, often with blood or pus
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Rectal pain
- Rectal bleeding — passing small amount of blood with stool
- Urgency to defecate
- Inability to defecate despite urgency
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Fever
- In children, failure to grow
Most people with ulcerative colitis have mild to moderate symptoms. The course of ulcerative colitis may vary, with some people having long periods of remission.
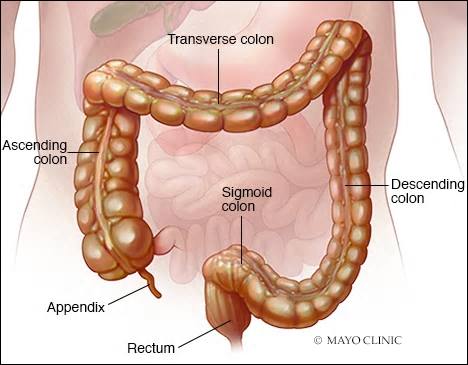
Types
Health care providers often classify ulcerative colitis according to its location. Types of ulcerative colitis include:
- Ulcerative proctitis. Inflammation is confined to the area closest to the anus (rectum), and rectal bleeding may be the only sign of the disease. This form of ulcerative colitis tends to be the mildest.
- Proctosigmoiditis. Inflammation involves the rectum and sigmoid colon (lower end of the colon). Signs and symptoms include bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramps and pain, and an inability to move the bowels in spite of the urge to do so (tenesmus).
- Left-sided colitis. Inflammation extends from the rectum up through the sigmoid and descending colon. Signs and symptoms include bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramping and pain on the left side, and unintended weight loss.
- Pancolitis. Pancolitis often affects the entire colon and causes bouts of bloody diarrhea that may be severe, abdominal cramps and pain, fatigue, and significant weight loss.
- Acute severe ulcerative colitis. This rare form of colitis affects the entire colon and causes severe pain, profuse diarrhea, bleeding, fever and inability to eat.
Meet people living with or caring for someone with digestive health concerns.
When to see a health care provider
See your doctor if you experience a persistent change in your bowel habits or if you have signs and symptoms such as:
- Abdominal pain
- Blood in your stool
- Ongoing diarrhea that doesn't respond to over-the-counter medications
- Diarrhea that awakens you from sleep
- An unexplained fever lasting more than a day or two
Although ulcerative colitis usually isn't fatal, it's a serious disease that, in some cases, may cause life-threatening complications.
Read more on the Mayo Clinic IBD blog, discussing the latest advances in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
This article is written by Mayo Clinic staff. Find more health and medical information on mayoclinic.org.
Related Articles