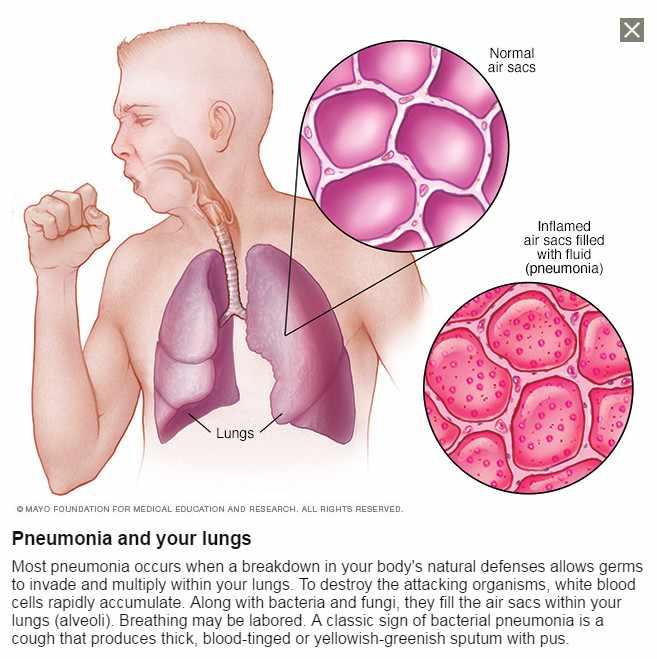
 Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus (purulent material), causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills and difficulty breathing. A variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses and fungi, can cause pneumonia.
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus (purulent material), causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills and difficulty breathing. A variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses and fungi, can cause pneumonia.
Causes
Many germs can cause pneumonia. The most common are bacteria and viruses in the air you breathe. Your body usually prevents these germs from infecting your lungs. But, sometimes, these germs can overpower your immune system — even if your health is generally good.
Pneumonia is classified according to the types of germs that cause it and where you got the infection.
Community-acquired pneumonia
Community-acquired pneumonia is the most common type of pneumonia. It occurs outside of hospitals or other health care facilities. It may be caused by:
- Bacteria The most common cause of bacterial pneumonia in the U.S. is Streptococcus pneumoniae. This type of pneumonia can occur on its own or after you've had a cold or the flu. It may affect one part (lobe) of the lung, a condition called lobar pneumonia.
- Bacteria-like organisms Mycoplasma pneumoniae also can cause pneumonia. It typically produces milder symptoms than do other types of pneumonia. Walking pneumonia is an informal name given to this type of pneumonia, which typically isn't severe enough to require bed rest.
- Fungi This type of pneumonia is most common in people with chronic health problems or weakened immune systems, and in people who have inhaled large doses of the organisms. The fungi that cause it can be found in soil or bird droppings, and vary depending on geographic location.
- Viruses Some of the viruses that cause colds and the flu can cause pneumonia. Viruses are the most common cause of pneumonia in children younger than 5. Viral pneumonia is usually mild. But, in some cases, it can become serious.
Treatment
Treatment for pneumonia involves curing the infection and preventing complications. People who have community-acquired pneumonia usually can be treated at home with medication. Although most symptoms ease in a few days or weeks, the feeling of tiredness can persist for a month or more.
Specific treatments depend on the type and severity of your pneumonia, your age and your overall health. The options include:
- Antibiotics These medicines are used to treat bacterial pneumonia. It may take time to identify the type of bacteria causing your pneumonia and choose the best antibiotic to treat it. If your symptoms don't improve, your doctor may recommend a different antibiotic.
- Cough medicine This medicine may be used to calm your cough so that you can rest. Because coughing helps loosen and move fluid from your lungs, it's a good idea not to eliminate your cough completely. In addition, you should know that few studies have looked at whether over-the-counter cough medicines lessen coughing caused by pneumonia. If you want to try a cough suppressant, use the lowest dose that helps you rest.
- Fever reducers/pain relievers You can take fever reducers/pain relievers as needed, such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB and others) and acetaminophen (Tylenol and others).







