-
Women’s Wellness: Problems with a posterior vaginal prolapse
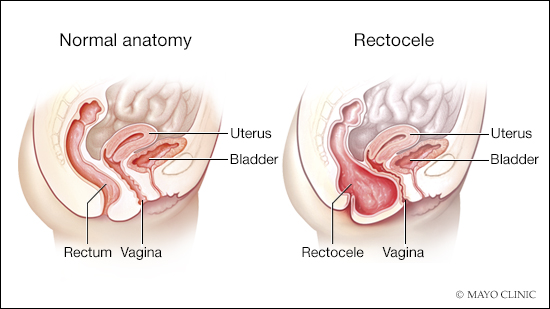
A posterior vaginal wall prolapse occurs when the thin wall of tissue that separates the rectum from the vagina weakens, allowing the vaginal wall to bulge. Posterior vaginal prolapse is also called a "rectocele"(REK-toe-seel).
Childbirth and other processes that put pressure on pelvic tissues can lead to posterior vaginal prolapse. A small prolapse may cause no signs or symptoms.
If a posterior vaginal prolapse is large, it may create a noticeable bulge of tissue through the vaginal opening. This bulge may be uncomfortable, but it's rarely painful.
If needed, self-care measures and other nonsurgical options are often effective. Severe posterior vaginal prolapse might require surgical repair.
Symptoms
A small posterior vaginal prolapse may cause no signs or symptoms.
Otherwise, you may notice:
- A soft bulge of tissue in your vagina that might protrude through the vaginal opening
- Difficulty having a bowel movement
- Sensation of rectal pressure or fullness
- A feeling that the rectum has not completely emptied after a bowel movement
- Sexual concerns, such as feeling embarrassed or sensing looseness in the tone of your vaginal tissue
Many women with posterior vaginal prolapse also experience prolapse of other pelvic organs, such as the bladder, uterus or — for women who have had a hysterectomy — the top of the vagina.
When to see a health care provider
Posterior vaginal prolapse is common — even in women who haven't had children. You may not even know you have posterior vaginal prolapse.
But sometimes moderate or severe posterior vaginal prolapses can be bothersome or uncomfortable. See your health care provider if:
- You have a bothersome bulge of tissue that protrudes through your vaginal opening
- Constipation treatment isn't successful at producing soft, easy-to-pass stool between three times a day to three times a week
Causes
Posterior vaginal prolapse results from pressure on the pelvic floor. Causes of increased pelvic floor pressure include:
- Chronic constipation or straining with bowel movements
- Chronic cough or bronchitis
- Repeated heavy lifting
- Being overweight or obese
Pregnancy and childbirth
The muscles, ligaments and connective tissue that support your vagina become stretched and weakened during pregnancy, labor and delivery. The more pregnancies you have, the greater your chance of developing posterior vaginal prolapse.
Women who have had only cesarean deliveries are less likely to develop posterior vaginal prolapse, but they still may.
Risk factors
Factors that may increase your risk of posterior vaginal prolapse include:
- Genetics
Some women are born with weaker connective tissues in the pelvic area, making them naturally more likely to develop posterior vaginal prolapse. - Childbirth
If you have vaginally delivered multiple children, you have a higher risk of developing posterior vaginal prolapse. If you've had tears in the tissue between the vaginal opening and anus (perineal tears) or incisions that extend the opening of the vagina (episiotomies) during childbirth, you also may be at higher risk. - Aging
As you grow older, you naturally lose muscle mass, elasticity and nerve function, causing muscles to stretch or weaken. - Obesity
Extra body weight places stress on pelvic floor tissues.
Prevention
To reduce your risk of worsening posterior vaginal prolapse, try to:
- Perform Kegel exercises regularly
These exercises can strengthen your pelvic floor muscles, which is especially important after you have a baby. - Treat and prevent constipation
Drink plenty of fluids and eat high-fiber foods, such as fruits, vegetables, beans and whole-grain cereals. - Avoid heavy lifting, and lift correctly
When lifting, use your legs instead of your waist or back. - Control coughing
Get treatment for a chronic cough or bronchitis, and don't smoke. - Avoid weight gain
Talk with your health care provider to determine your ideal weight and get advice on weight-loss strategies, if you need them.
This article is written by Mayo Clinic staff. Find more health and medical information on mayoclinic.org.







