-
Mayo Clinic Q and A: Uterine polyps rarely are cancerous
 DEAR MAYO CLINIC: I have a few small uterine polyps that my health care provider says are not likely to be cancerous and that I could be reevaluated in six months to see if further testing is needed. Is it common for uterine polyps to turn into cancer? I am 49.
DEAR MAYO CLINIC: I have a few small uterine polyps that my health care provider says are not likely to be cancerous and that I could be reevaluated in six months to see if further testing is needed. Is it common for uterine polyps to turn into cancer? I am 49.
ANSWER: It is rare for uterine polyps to be cancerous. If they aren’t causing problems, monitoring the polyps over time is a reasonable approach. If you develop symptoms, such as abnormal bleeding, however, then the polyps should be removed and evaluated to confirm that there is no evidence of cancer.
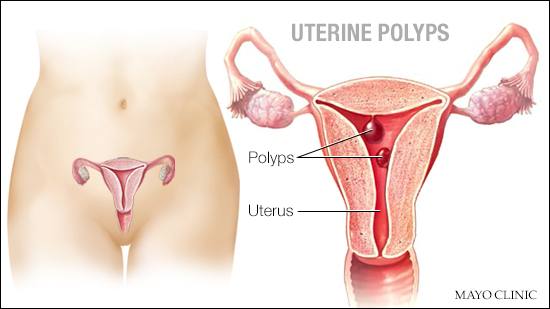
A uterine polyp is a growth that is attached to the inner wall of the uterus. Uterine polyps form when there’s an overgrowth of cells in the lining of the uterus, called the endometrium. These polyps can range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters. It’s not clear exactly what triggers the development of uterine polyps, but hormonal factors appear to play a role. Uterine polyps most commonly occur in women who are going through, or have completed, menopause, although younger women can get them, too.
The odds of a uterine polyp being cancer or becoming cancerous are low. In premenopausal women, that number is 1-2 percent. In women who have gone through menopause, the risk is 5-6 percent. But even with the low risk, health care providers often will take a tissue sample of a uterine polyp for lab testing. That’s because some uterine cancers or precancerous changes of the uterus, such as endometrial hyperplasia, may first appear as uterine polyps.
If the biopsy shows there’s no cancer or precancerous cells — and the polyps aren’t causing any symptoms — additional treatment isn’t necessary. In some cases, small uterine polyps may go away on their own.
If you notice symptoms that could be related to the polyps, make an appointment to see your health care provider promptly. The most common symptom of uterine polyps is abnormal vaginal bleeding, including unusually heavy periods, frequent or unpredictable periods, bleeding between periods, or vaginal bleeding after menopause.
When polyps trigger symptoms, it’s typically recommended that the polyps be removed during a minor surgical procedure called a ‘hysteroscopic polypectomy.’ The procedure can be performed in your doctor’s office without anesthesia or in an operating room with anesthesia. If you are advised that the polyps should be removed, have a conversation with your health care provider about which approach is right for you.
During a hysteroscopic polypectomy, your doctor inserts a small, thin, lighted telescope, called a “hysteroscope,” through your vagina and cervix into your uterus. This enables your doctor to see into the uterus and identify the polyps. Your doctor then inserts surgical instruments through the hysteroscope to remove the polyps.
After they’ve been removed, the polyps are sent to a laboratory for evaluation to confirm that they are noncancerous. If a uterine polyp does contain cancerous or precancerous cells, your health care provider will talk with you about the next steps in evaluation and treatment.
In most cases, however, uterine polyps do not pose additional health risks. Removing them resolves abnormal bleeding, and it’s uncommon for polyps to recur. After uterine polyps have been removed, most women do not need further treatment. — Dr. Christopher Destephano, Obstetrics and Gynecology, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Florida







