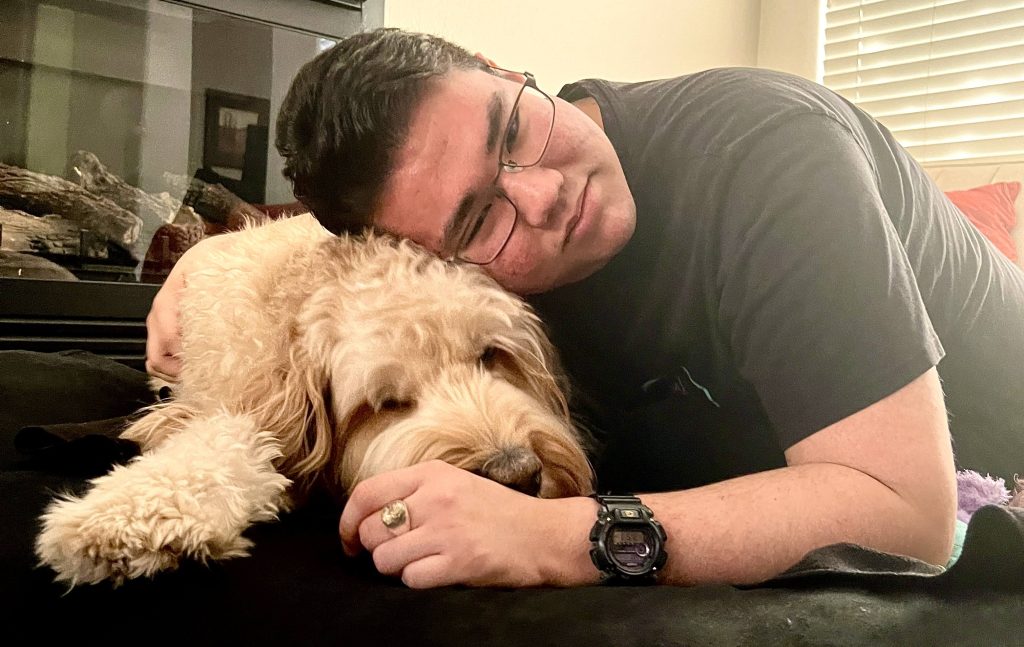
For Anthony Maita, 'Buddy' is not just any other dog.
"He's the best thing that's ever happened to me," says Anthony.
It's no wonder, considering Buddy was right by Anthony's side during one of the most challenging times of his life — when Anthony began having epileptic seizures.
Watch: When seizures don't stop: Anthony's battle against drug-resistant epilepsy
Journalists: Broadcast-quality video (2:38) is in the downloads at the end of this post. Please courtesy: "Mayo Clinic News Network." Read the script.
"I started having the seizures, noticeable seizures, and from there, it just started getting worse and worse," recalls Anthony.
It began after Anthony graduated from high school. He was making plans for his future and looking forward to attending college. That's when the seizures began.
Initially, the seizures were mild but quickly became more severe. "The experience (seizure) is like a loss of time, like a blank spot in your memory — like you're waking up without any recollection of what happened," says Anthony.
"The seizures were several times a week. His lips would be blue. His mouth would be blue," says Patricia Maita, Anthony's mother. "It so hard to see your child go through that and feel so helpless."
Doctors tried to manage Anthony's seizures with medication, but nothing worked. Eventually Anthony was diagnosed with drug-resistant epilepsy, or DRE.
In search of hope, Anthony's family turned to Mayo Clinic in Arizona.
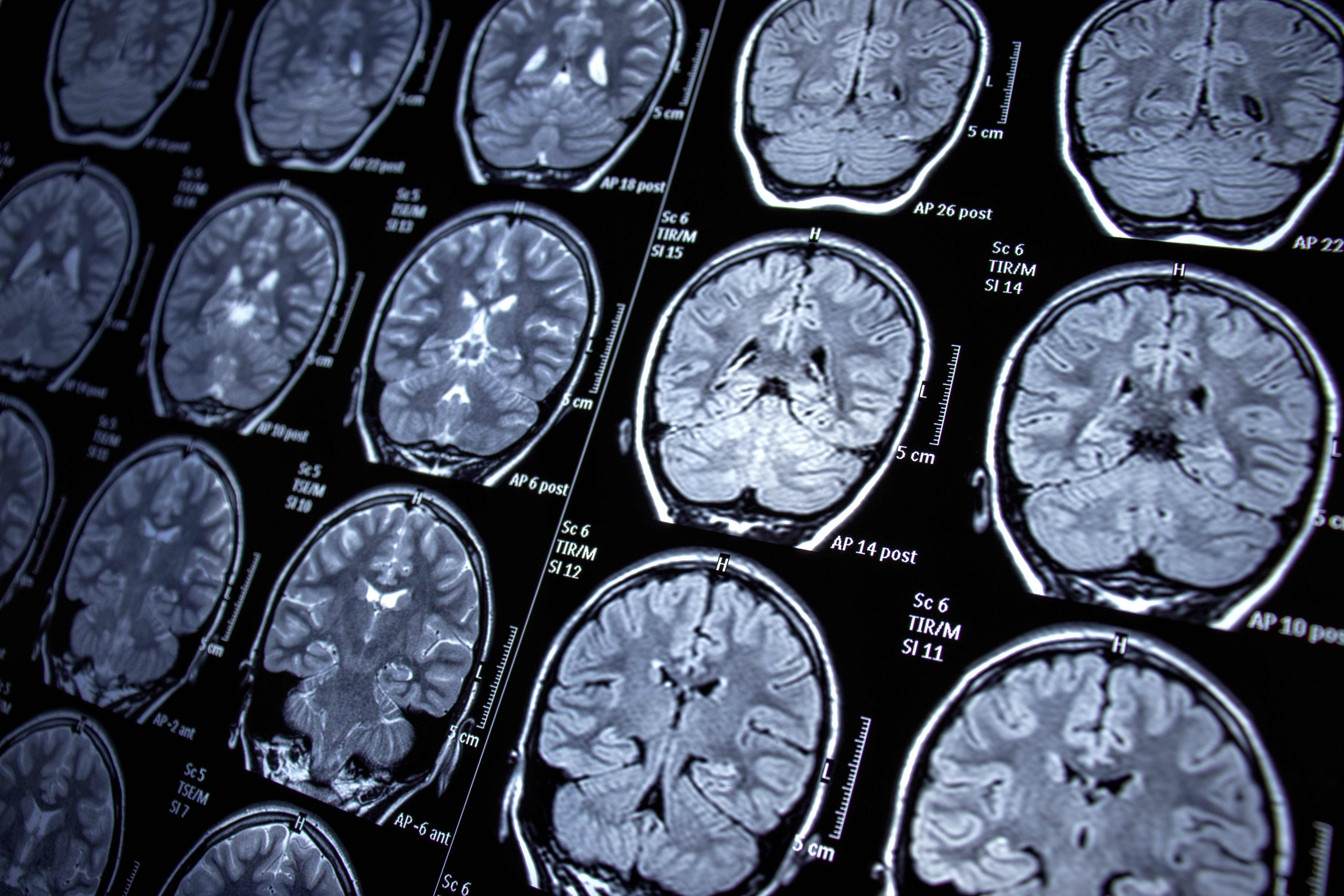
"Up to a third of patients who develop epilepsy during their life will become resistant to medication," explains Jonathon J. Parker, M.D., Ph.D., a neurosurgeon at Mayo Clinic who specializes in treating the most serious and complex cases of epilepsy, including DRE.
"These patients have tried at least two medications, and they're still having seizures. At that point, we know the chances of seizure freedom unfortunately become very low, and that's when we start looking at other options," says Dr. Parker.
A battle for millions worldwide
Anthony is one of approximately 50 million people worldwide diagnosed with epilepsy. It is one of the most common neurological disorders globally. It is characterized by recurrent unprovoked seizures caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
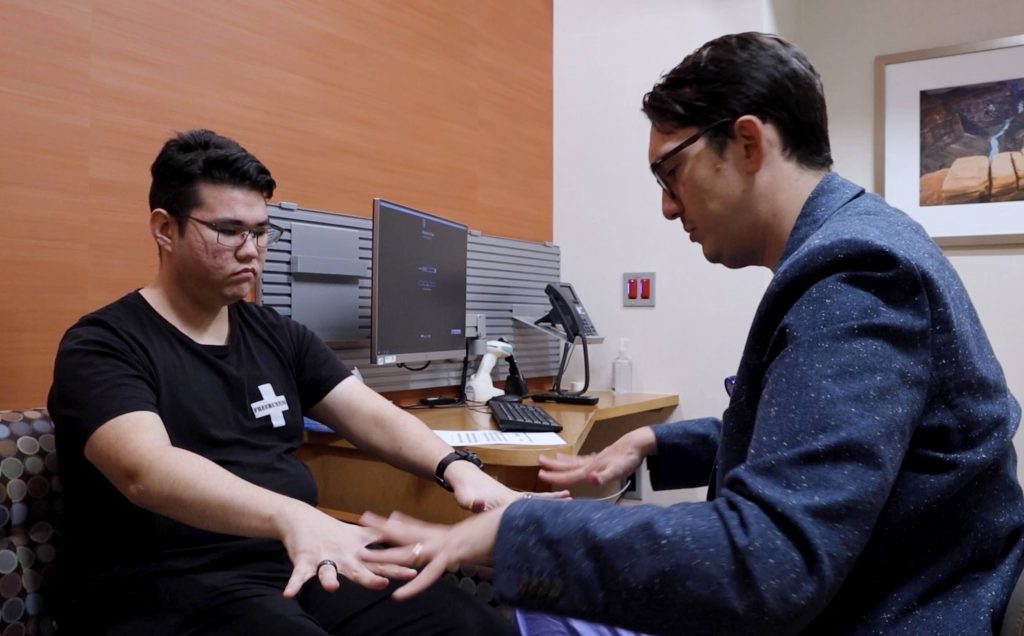
Of those diagnosed with epilepsy, approximately 30%, or 15 million people, are considered medication-resistant. Uncontrolled seizures often rob many people of their ability to live and function independently.
While it is rare, seizures can lead to sudden unexplained death in epilepsy, or SUDEP. "We know that more frequent seizures mean the patient is at higher risk of SUDEP, so that's why we are very aggressive about treating epilepsy with all the tools we have available," says Dr. Parker.
Current treatment options for patients with DRE include surgical procedures such as brain resection to remove a portion of the brain tissue responsible for generating seizures. A less invasive procedure involves laser ablation therapy that pinpoints and destroys abnormal brain tissue. While often effective, these surgical approaches carry the risk of possible side effects, such as memory impairment, motor deficits and speech difficulties.
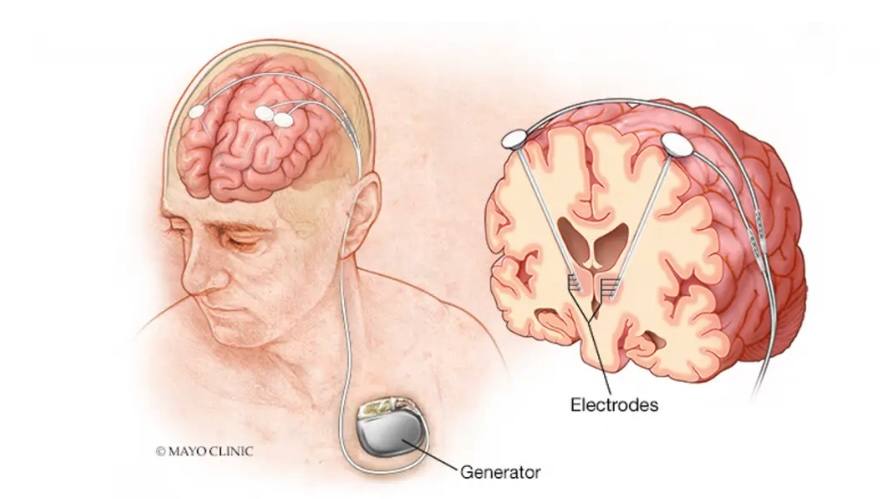
Neuromodulation is another surgical approach that uses electrical or magnetic stimulation to interrupt abnormal neural activity without removing brain tissue.
Unlocking new hope for patients
Now, a growing number of scientists across the globe are part of an innovative trend in research, investigating novel ways to treat DRE. It involves the use of regenerative medicine as a "reparative" approach to help the brain heal.
Dr. Parker is the lead investigator of the first-in-human clinical trial at Mayo Clinic which studies the use of implanted specialized inhibitory brain cells as a potential reparative treatment for DRE. Dr. Parker's clinical trial is underway in Arizona.
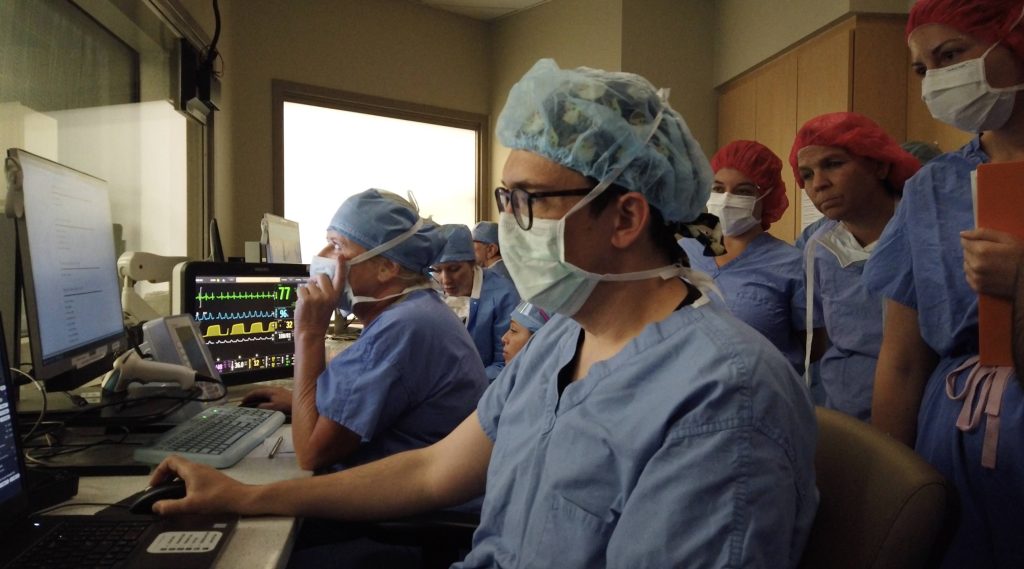
"This is an exciting time for regenerative medicine and the potential it may have for millions of people who suffer from the debilitating side effects of drug-resistant epilepsy."
Dr. Jonathon J. Parker, neurosurgeon and clinical trial lead investigator
Mayo Clinic in Arizona is one of 29 sites nationwide participating in the inhibitory brain cell implant clinical trial for patients with focal epilepsy, where seizures originate in a specific region of the brain.
Anthony became Mayo Clinic's first patient to undergo the investigational brain cell implant.
"We use a very minimally invasive technique where we inject the inhibitory cells through a pencil eraser-sized incision in the back of the head. Our hope is that, over time, these cells become part of the brain and help repair the neural circuitry, and reduce or prevent seizures without the side effects," says Dr. Parker. The cells are implanted in a one-time, single-dose procedure.
"Honestly, it was pretty easy," says Anthony. "I had no trouble with it." Anthony was discharged from the hospital the next day.
Doctors say it is still too early to determine whether the brain cell implant was effective, but they are hopeful.
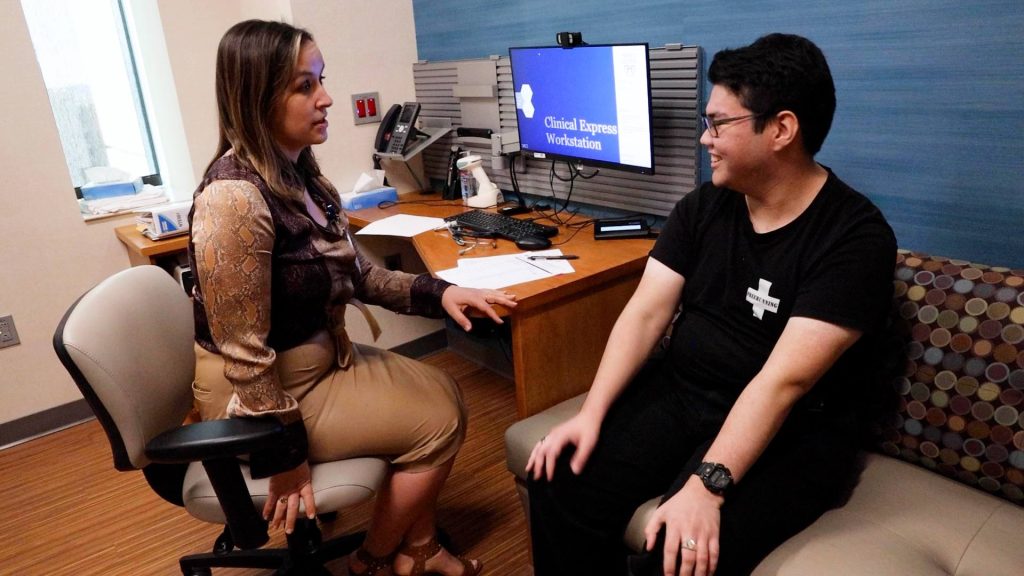

"Anthony has been doing great since the procedure," says Dr. Amy Z. Crepeau, a neurologist at Mayo Clinic. "We have a great deal of optimism in regard to the potential of this brain cell therapy. Developing a safe and effective, minimally invasive treatment that does not carry the possible negative side effects could be a game changer in treating patients with DRE and improving their quality of life."
Tabitha's life-long struggle to control seizures
Tabitha Wilson lives in fear, never knowing when or where the next seizure will strike.
The Florida resident was diagnosed with epilepsy at the age of 2. She was placed on medication that adequately managed her seizures — until the week before her high school graduation.

"I was 17 years old sitting in history class when the seizure happened," recalls Tabitha. "They had to load me up in an ambulance in front of the whole school."
"It was traumatizing. Something I will never forget."
Tabitha Wilson describing her seizure during class in high school
Tabitha tried new types of medications, but the seizures only got worse.
"I fell down a flight of stairs, burned myself while cooking. I've completely blacked out and don't know where I am or who you are," says Tabitha. She was eventually diagnosed with drug-resistant epilepsy.
Tabitha underwent three brain surgeries to treat her DRE. Still, the seizures continued.
"I'll have good days and bad days. Some days, I'll have two, three, four seizures, back-to-back," says Tabitha.

Photo courtesy: Tabitha Wilson
Her uncontrolled seizures have robbed Tabitha of the ability to live independently. "I can't drive. I can't cook. I can't go swimming alone. I can't take a bath, only a shower and if someone is home with me," says Tabitha.
Watch: Tabitha Wilson shares what it's like to live with drug-resistant epilepsy.
Tabitha turned to Mayo Clinic in Florida where she learned about a clinical trial also investigating the potential of regenerative medicine as a possible treatment for DRE.
Dr. Sanjeet S. Grewal, director of stereotactic and functional neurosurgery at Mayo Clinic, is leading a team of researchers studying the use of implanted stem cells in conjunction with deep brain stimulation for patients like Tabitha.
Deep brain stimulation is one of the most recent FDA-approved methods of neuromodulation therapy for epilepsy. Studies show that patients who undergo deep brain stimulation experience median seizure reduction up to 70% after five years. However, Dr. Grewal says it is uncommon for patients to become seizure-free.
"Unfortunately, neuromodulation doesn't give us the seizure freedom we want, and that's why we are trying to combine deep brain stimulation with stem cell therapy to see if we can increase the efficacy of neuromodulation," he says.
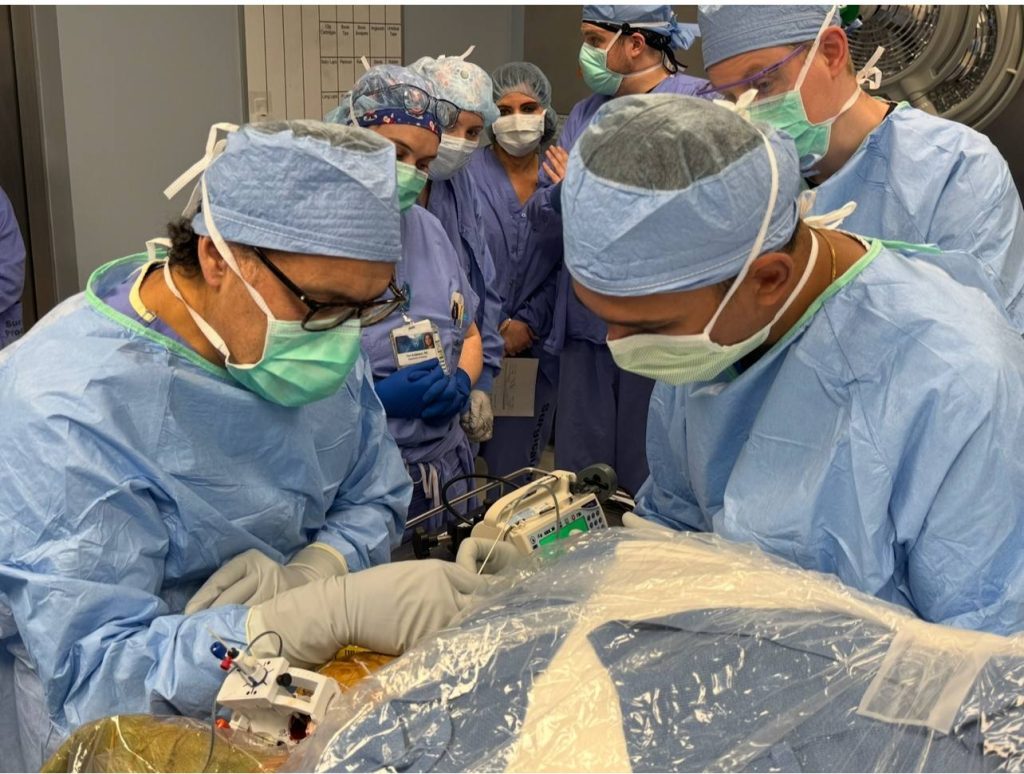
Tabitha became the first patient to undergo the investigational treatment. Dr. Grewal says she is also the first person in the world to undergo surgery for deep brain stimulation and receive stem cell therapy in the thalamus in her brain as a potential treatment for DRE.
Watch: Dr. Sanjeet Grewal, neurosurgeon, explains how Mayo researchers are leading a new trend in research for treating patients with drug-resistant epilepsy.
The clinical trial involves the use of mesenchymal stem cells, a type of adult stem cell that has anti-inflammatory properties. MSCs may also support tissue repair and healing. Further scientific research is needed to confirm their therapeutic potential in the field of regenerative medicine.
"There are some patients whose seizures are just much harder to treat with the technology we have today. Our hope is that by adding stem cells and their regenerative potential, we can increase treatment success."
Dr. Sanjeet Grewal, Neurosurgeon and Clinical trial lead investigator
The MSCs used in the clinical trial are derived from fat tissue and created at the Human Cell Therapy Laboratory at Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Florida under the leadership of Abba Zubair, M.D., Ph.D., a pioneer in cell therapy.
Dr. Zubair's research teams have developed a cost-effective method of producing MSCs for use in potential treatments for conditions such as stroke.
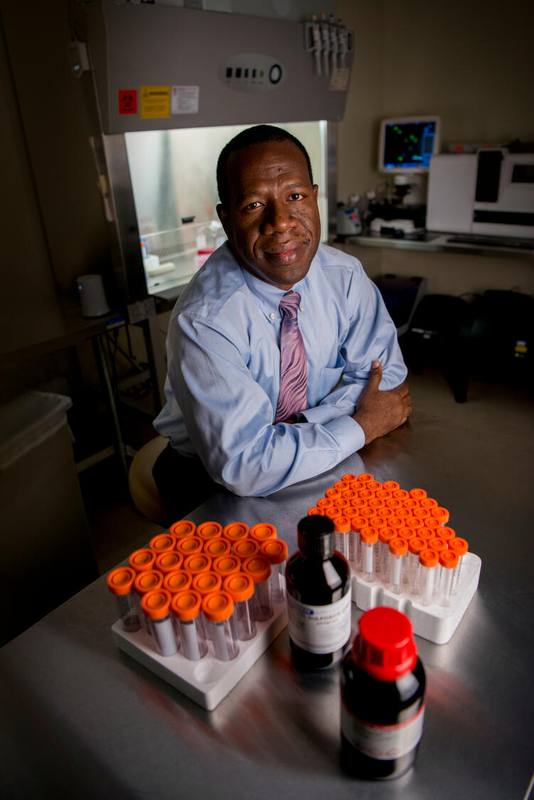
"My mission is to discover ways to address problems that patients have been struggling with and find a solution for them.
Dr. Abba Zubair, Pioneer in Cell therapy, Mayo Clinic in Florida
I believe the future is bright. "
Dr. Zubair has several research projects scheduled to launch into space in 2025.
"MSCs are what we call multipotent, meaning they can differentiate into different cell types based on where they're placed. If they are placed near blood vessels, they can become blood vessel types. If they're placed by heart cells, they can become heart cell types," explains Dr. Grewal.
The hope is the MSCs eventually become neural or brain cell types and interact in the part of the brain where the seizures occur. "It's called paracrine signaling, where they're releasing signals to the brain tissue around them and interacting in a way to try to repair that tissue."
"I'm willing to try everything and anything to get some sort of control over these seizures because I've been living with this for so long."
Tabitha Wilson, Clinical Trial participant
Since undergoing the procedure, there has been an improvement in Tabitha's seizure management. However, Dr. Grewal says it is too early to know whether this is due to the deep brain stimulation, stem cells or both.
Drs. Grewal and Parker say there is still a long road ahead to determine whether these cell therapies are proven safe and effective for patients with DRE. But they agree each day brings them one step closer to a potential treatment or cure for patients like Tabitha and Anthony.
"We've thought about this for generations, we just didn't have these technologies to enable it. Now we do," says Dr. Grewal. "So, whether it's wound healing, neurodegeneration, epilepsy or stroke, there are so many different studies going on investigating the potential of regenerative or reparative therapies."
Related articles
- Mayo Clinic researchers lead transformative shift toward neurorestorative treatment strategies for most severe forms of epilepsy
- Epilepsy Treatment
- Minimally invasive epilepsy treatment
- Mayo Clinic Minute: Demystifying epilepsy
- Epilepsy Surgery
- Laser ablation surgery helps treat young man’s epilepsy