-
Mayo Clinic Minute: Can uterine fibroids affect pregnancy?
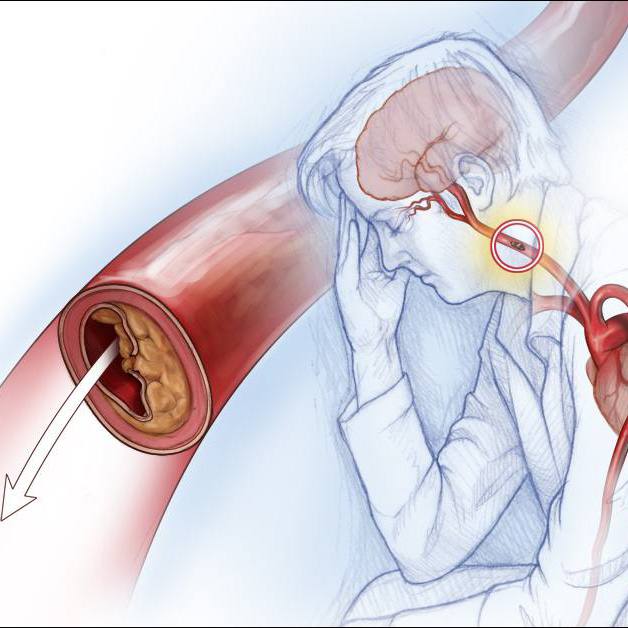
A uterine fibroid is a benign or noncancerous growth of the muscle portion of the uterus. While common, they may cause pain and excessive bleeding, and concerns about fertility and pregnancy for some.
Dr. Michelle Louie, a Mayo Clinic gynecologic surgeon and fibroid specialist, says it is important to know your treatment options and work with a specialist.
Journalists: Broadcast-quality video (0:57) is in the downloads at the end of this post. Please courtesy: "Mayo Clinic News Network." Read the script.
Fibroids can go undetected in many healthy pregnancies.
"But depending on their size or location, they may affect a person's ability to get pregnant, or stay pregnant or have a healthy pregnancy," says Dr. Louie.
Fibroids are usually classified based on their location in the uterus, for instance.
"A submucosal fibroid is most likely to affect a future pregnancy or affect a person's ability to get pregnant or conceive; whereas, intramural fibroids, especially if they're small, would probably have no effect on a future pregnancy or person's ability to get pregnant," she says.
An ultrasound or MRI may be ordered to assess treatment options.
"The traditional surgery that's evidence-based for people who are wanting future pregnancy is a myomectomy."
Dr. Louie says fibroids may complicate pregnancy for some. "Fibroid specialists may be very much able to guide them to the variety of treatment options that we have — both to allow treatment of their symptoms and to allow future childbearing if that's one of their goals."
Related post:
Related Articles